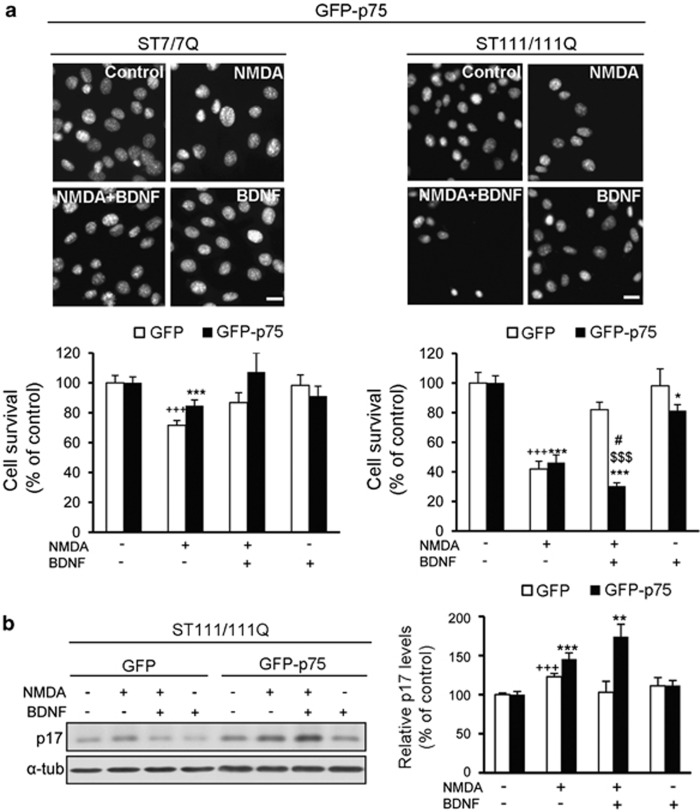
Figure 6.
BDNF fails to protect GFP-p75 STHdh111/111Q mutant cells against NMDA excitotoxicity. Wild-type (ST7/7Q) and mutant (ST111/111Q) huntingtin striatal cells transfected with GFP or GFP-p75 were treated with BDNF (50 ng/ml, 30 min), NMDA (500 μℳ, 30 min) or BDNF before addition of NMDA (NMDA+BDNF) and cell survival was evaluated 24 h later by scoring the percentage of Hoechst-stained nuclei. (a) Representative photomicrographs of wild-type and mutant huntingtin striatal cells stained with Hoechst showing the number of surviving cells in the different conditions (Control, NMDA, NMDA+BDNF and BDNF) Scale bar, 10 μm. Quantification of surviving cells is shown as the percentage of total cells in control conditions (vehicle). The results are representative of seven independent experiments performed in triplicate and are expressed as the mean±S.E.M. Data was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Student's t-test. +++P<0.001 versus vehicle-treated GFP cells, *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 versus vehicle-treated GFP-p75 cells, #P<0.05 NMDA-treated GFP-p75 cells versus NMDA+BDNF-treated GFP-p75 cells, $$$P<0.001 NMDA+BDNF-treated GFP mutant cells versus NMDA+BDNF-treated GFP-p75 mutant cells. (b) Mutant huntingtin cells (ST111/111Q) transfected with GFP or GFP-p75 were treated with BDNF, NMDA or BDNF before NMDA and cell extracts obtained 3 h later. Immunoblots were performed to detect cleaved caspase-3 (p-17 fragment) and α-tubulin as loading control. The blot is representative of four independent experiments. The histogram represents the relative p-17 levels considering 100% the value obtained in control conditions (vehicle). Values are given as mean±S.E.M. Data was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Student's t-test. +++P<0.001 versus vehicle-treated GFP mutant cells and **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus vehicle-treated GFP-p75 mutant cells