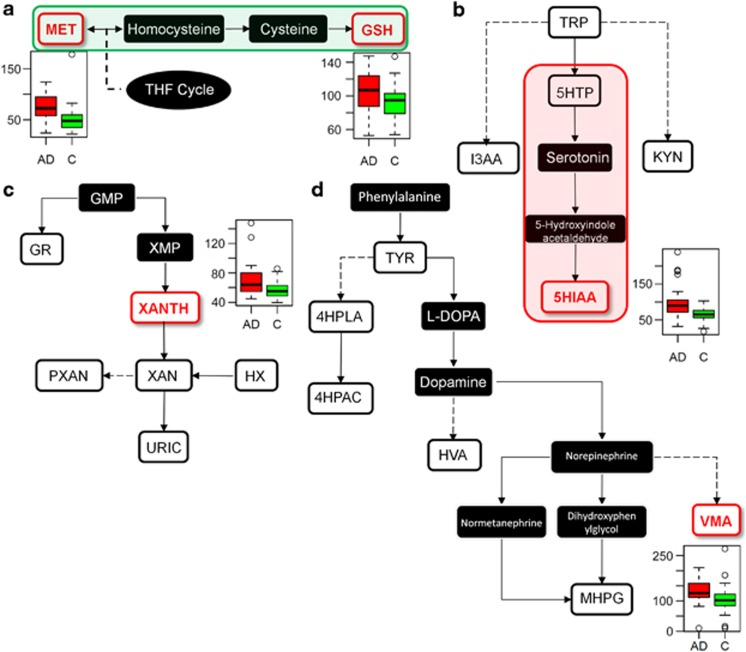
Figure 1.
Changes in the methionine (a), tryptophan (b), purine (c) and tyrosine (d) pathways in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Red metabolites: significantly increased in AD; dark metabolites: not measured. Red and green pathways: significantly up- and downregulated in AD, respectively, implicated by ratios. For expansions of the metabolite abbreviations, see Table 2.