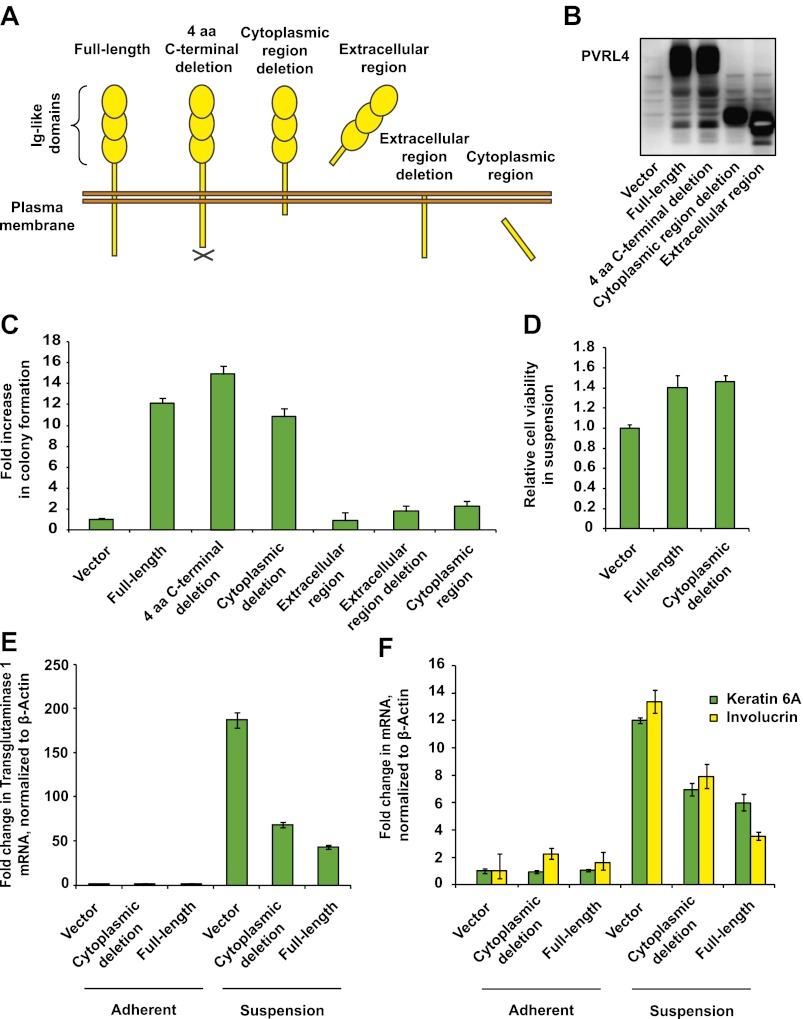
Figure 2. PVRL4-induced anchorage-independent colony formation is carried out through its extracellular region.
(A) and (B) A series of PVRL4 deletion constructs were designed and their expression confirmed by Western blot. (C) PVRL4 mutants from (A) were tested for their ability to induce anchorage-independent colony formation in triplicate (error bars ± SD). (D) Cells with full-length PVRL4 or the cytoplasmic region deletion mutant were assayed for viability under conditions of anchorage deprivation by measuring total ATP content in cells cultured on ultra-low attachment plates for 72 hr. Values were normalized to an empty vector-transduced sample. Assays were performed in triplicate (error bars ± SD). (E) and (F) TL-HMECs expressing empty vector, full-length PVRL4 or cytoplasmic region deletion mutant containing cells were cultured on tissue culture-treated (adherent) or ultra-low attachment (suspension) dishes for 72 hr. RNA was isolated and mRNA levels for TGM1 (E) and KRT6A and IVL (F) were measured by RT-qPCR. Transcript levels were normalized to β-actin. qPCR was performed in quadruplicate (error bars ± SD).