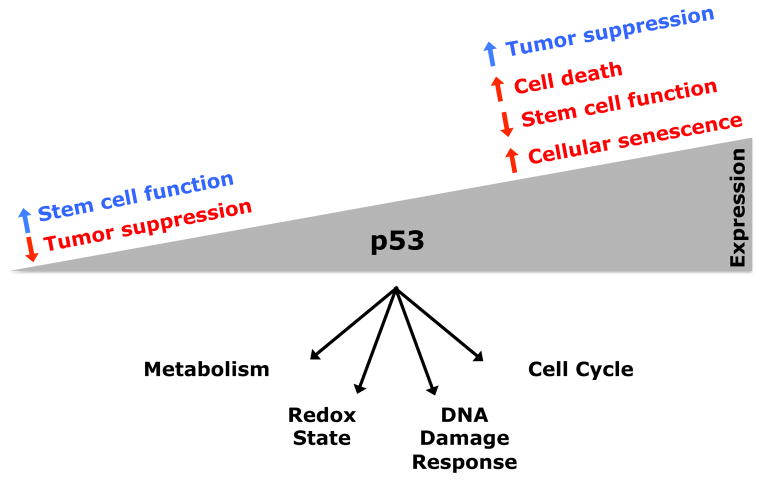
Figure 3. The Multifaceted and Context-Dependent Effects of p53 in Stem Cells.
The consequences of tumor suppressor expression in stem cells can be context dependent. p53 can have both positive (blue) and negative (red) effects on stem cell function, depending on context and expression level. When expressed at low levels, p53 can promote stem cell maintenance by promoting the maintenance of genomic integrity and by regulating metabolism. When expressed at high levels, p53 can promote stem cell depletion through cell death or cellular senescence. The aggregate effect of these functions influences longevity, cancer incidence, and tissue regeneration during aging (Tyner et al., 2002; TeKippe et al., 2003; van Heemst et al., 2005; Dumble et al., 2007; Schoppy et al., 2010; Gannon et al., 2011).