Fig. 1.
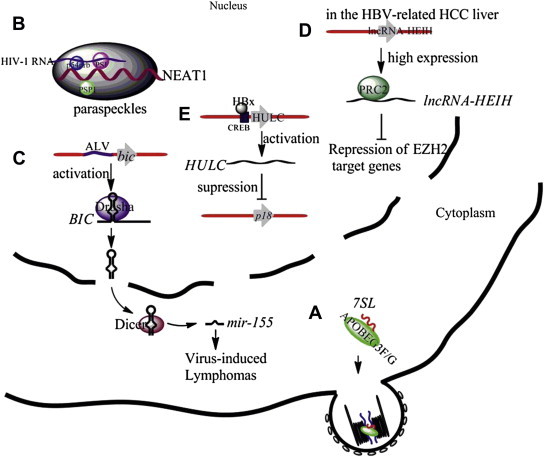
Illustrations of the functions of selected cellular lncRNAs in virus-infected cells. (A) The cytidinedeaminase APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F selectively interact with 7SL RNAs and are incorporated into virions. (B) The lncRNA NEAT1 serves as a structural scaffold for the nuclear substructure paraspeckles. Paraspeckle proteins PSF and p54nrb bind to HIV-1 RNA and retain the RNA in paraspeckles. (C) The integrated ALV activates bic gene expression by promoter insertion. BIC RNA, the precursor of miR-155, is suggested to be responsible for virus-induced lymphomas. (D) The lncRNA-HEIH, which is highly expressed in HBV-related HCC, recruits the PRC2 complex to repress EZH2 (an important subunit of the PRC2 complex) targeted genes. (E) HULC is upregulated by HBx protein through activation of the HULC promoter via CREB, leading to the suppression of the tumor suppressor gene p18. ALV = avian leukosis virus; CREB = cAMP responsive element binding protein; EZH2 = enhancer of zeste homolog 2; HBV = hepatitis B virus; HBx = hepatitis B virus X; HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma; lncRNAs = long noncoding RNAs; lncRNA-HEIH = lncRNA high expression in HCC; HULC = lncRNAs highly upregulated in liver cancer; PRC2 = polycomb repressive complex 2.
