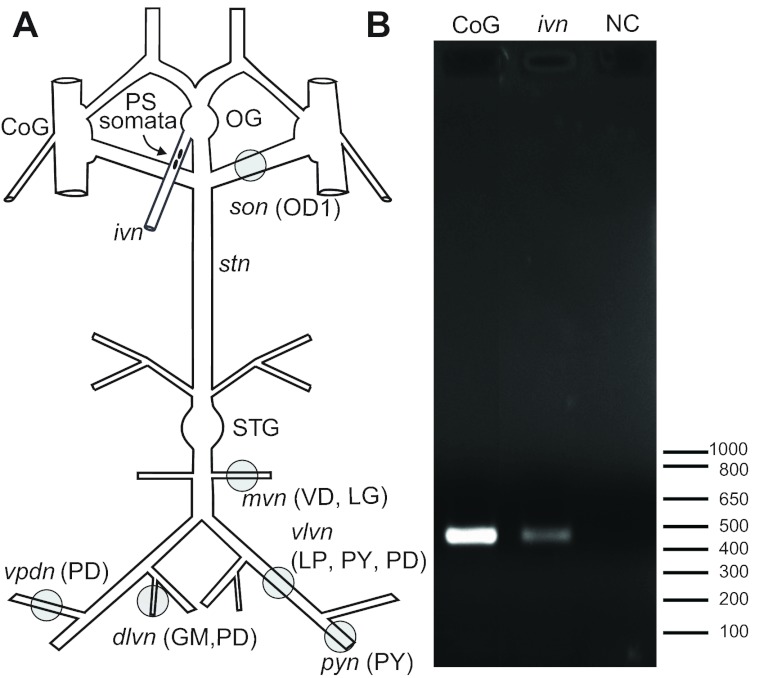
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the Homarus americanus stomatogastric nervous system (STNS) and RT-PCR profiling of crustacean myosuppressin (Crust-MS) transcript in the pyloric suppressor (PS) neurons of the lobster. (A) Schematic representation of the lobster STNS showing the location of the PS neuron somata, as well as the locations of extracellular nerve recordings (grey circles) and the neurons recorded from each nerve. (B) RT-PCR profiling of Crust-MS transcript in the PS neurons indicates that the FLRFamide-like peptide in these neurons is Crust-MS. Using a gene-specific primer set, a robust band of the predicted Crust-MS PCR amplicon (459 bp in length) was consistently detected in the inferior ventricular nerve (ivn; Lane 2), the location of the PS neurons in Homarus, as well as in the commissural ganglion (CoG; Lane 1), a known source of Crust-MS peptide (Stemmler et al., 2007). In contrast, no product was detected in the negative (no cDNA) control (NC; Lane 3). Other abbreviations: dlvn, dorsal lateral ventricular nerve; GM, gastric mill neuron; LG, lateral gastric neuron; LP, lateral pyloric neuron; mvn, medial ventricular nerve; OD1, oesophageal dilator 1 neuron; OG, oesophageal ganglion; PD, pyloric dilator neuron; PY, pyloric neuron; pyn, pyloric nerve; son, superior oesophageal nerve; STG, stomatogastric ganglion; stn, stomatogastric nerve; VD, ventral dilator neuron; vlvn, ventral lateral ventricular nerve; vpdn, ventral pyloric dilator nerve.