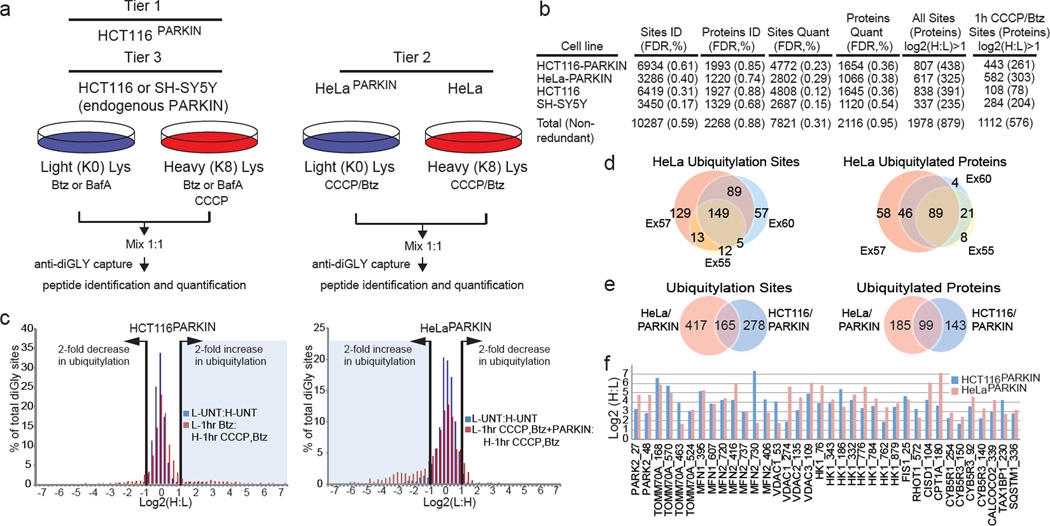
Figure 1. QdiGLY proteomics for PARKIN-dependent ubiquitylation.
a, Proteomics work flow. b, diGLY sites identified and quantified across 73 experiments. FDR, false discovery rate. c, log2(H:L) plots for quantified diGLY peptides for HCT116PARKIN (experiment 17) or HeLaPARKIN (experiment 57) cells (Table S2). d, Overlap of ubiquitylation sites in HeLaPARKIN biological triplicates (1h CCCP + Btz) (Table S1, S2). e, Ubiquitylation site and protein overlap between all HCT116PARKIN and HeLaPARKIN experiments treated with CCCP and Btz for 1h. f, log2(H:L) ratios for selected diGLY sites from HCT116PARKIN (Ex 17) and HeLaPARKIN (Ex 57) (1h CCCP + Btz).