Fig. 2.
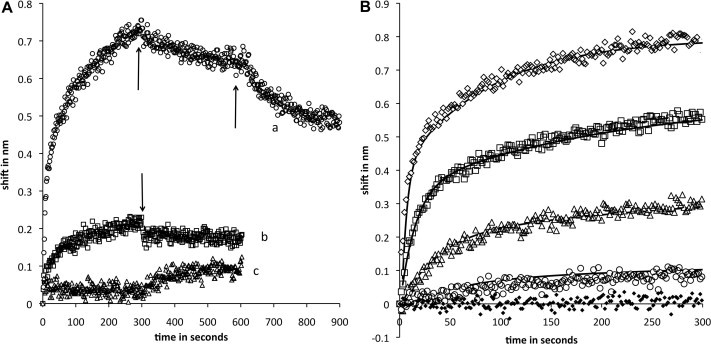
(A) Sensorgrams of eNOS and nNOS binding to p38. Immobilized p38 was immersed in 696 nM NOS at time 0. Binding was measured for 300 s followed by transfer to buffer only and monitoring of dissociation for 300 s. Trace a (circles), eNOS binding with an additional step in which the tip was moved into buffer with 1 μM CaM after initial dissociation. Trace b (squares), nNOS binding. Trace c (triangles), eNOS pre-equilibrated with a fourfold molar excess of CaM prior to immersion of p38. Arrows indicate movement of sensors from association to dissociation or dissociation to CaM-containing buffer. (B) Sensorgrams of eNOS concentration course. eNOS concentrations in nM units were 696 (open diamonds), 232 (squares), 77 (triangles), 26 (circles) and 0 (black diamonds). Fits to a two-component sequential model are shown as solid lines. Dissociation phases were similar to trace a in Fig. 1. Kinetics parameter sets for successive traces in order of decreasing eNOS were 0.1, 0.01, .006, .001; 0.03, 0.01, 0.0002, 0.001; 0.0008. 0.01, 0.006, 0.001; 0.0025, 0.01, 0.0002, 0.001 in sec-1 for k1, k2. k3, and k4.
