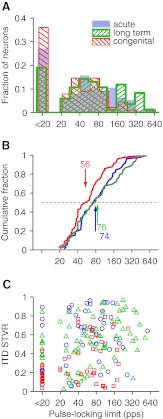
FIG. 10.
Pulse-locking limits are lower in congenitally deaf cats than acutely or long-term deafened cats. A Distribution of pulse-locking limits compared across three deafness groups. Bin labeled “<20 pps” represents neurons that were not pulse-locked at any pulse rate. B Corresponding cumulative distributions. C Pulse-locking limit does not predict degree of neural ITD sensitivity.