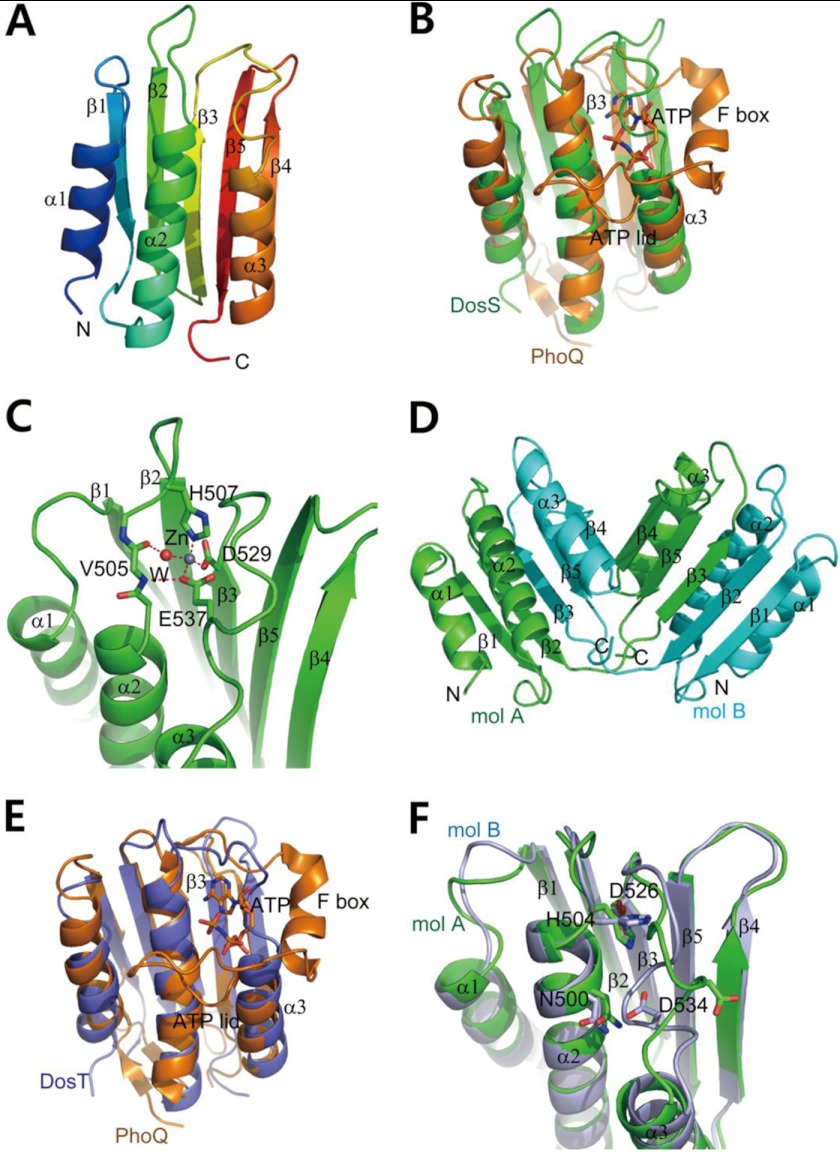
FIGURE 2.
Crystal structures of DosS ABD and DosT ABD. A, ribbon diagram of the structure of the DosS ABD showing an α/β-sandwich fold. Three helices are one side of a mixed β-sheet, with strand order 1-2-3-5-4. Protein regions are colored from blue to red from the N to C terminus. B, superimposition of the DosS ABD (green) on the PhoQ ABD (orange) bound to an ATP analog. The ATP is surrounded by the F box helix and long ATP lid. A loop connecting β3 and α3 in the DosS ABD overlies the ATP binding site. C, A zinc ion found in the DosS ABD is coordinated by His507, Glu537, and Asp529, and a water molecule, which is hydrogen-bonded to the carbonyl oxygen of Val505. This interaction holds the position of the loop connecting β3 and α3 via Glu537. D, ribbon diagram of a DosT ABD dimer from the crystal structure showing domain swapping. The C-terminal parts (from the β3 strand to the C terminus) of two molecules (mol; green and cyan) were swapped. The two DosT ABDs reconstituted by switching C-terminal region are almost identical to one another. E, superimposition of the DosT ABD (blue) on to the PhoQ ABD (orange) bound to ATP. The loop connecting β3 and α3 in the DosT ABD overlies the ATP binding site. F, superimposition of two DosT ABDs. The orientations of the Asp534 side chains in the loops connecting β3 and α3 are opposite when the loop is rotated.