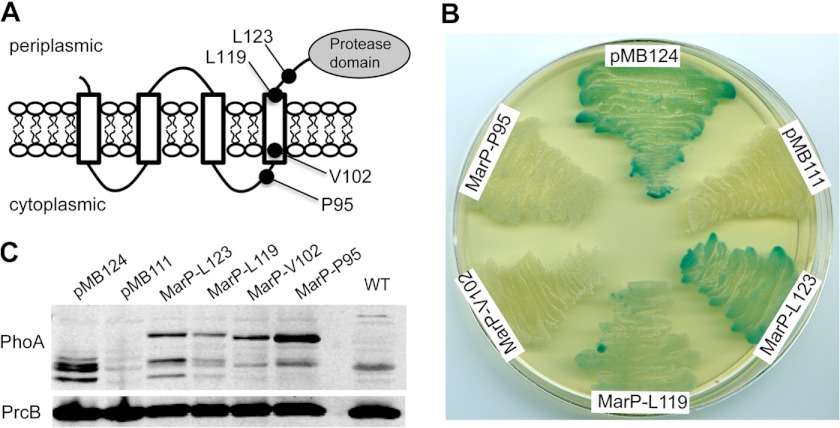
FIGURE 1.
Membrane topology of the protease MarP. A, shown is a model of MarP topology. Black circles indicate the location of the PhoA fusions that were created at residues Leu-123, Leu-119, Val-102, and Pro-95. B, alkaline phosphatase activity of M. smegmatis strains expressing MarP-PhoA fusion proteins are shown. Strains were plated on LB agar containing the alkaline phosphatase substrate 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate. Plasmid pMB124 (positive control) expresses PhoA fused to the signal sequence of Mtb antigen 85B, and pMB111 (negative control) expresses PhoA without a signal sequence; MarP-Leu-123, MarP-Leu-11, MarP-Val-102, and MarP-Pro-95 express PhoA fused to the respective residues of MarP. C, shown is an immunoblot of M. smegmatis lysates probed with a PhoA-specific monoclonal antibody (α-PhoA). An immunoblot for the proteasome subunit B (α-PrcB) serves as loading control.