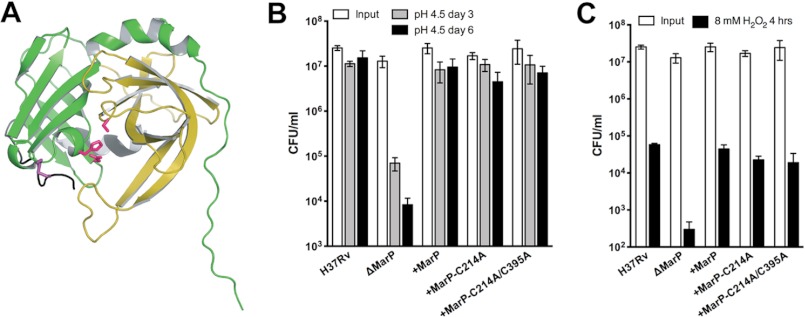
FIGURE 7.
Importance of the MarP disulfide bond for survival of Mtb exposed to acid and oxidative stress. A, a schematic representation of the MarP protease domain (PDB ID 3K6Y) shows the location of the disulfide bond between Cys-214 and Cys-395 (purple). The active site residues are shown in pink. The disulfide bonds links the N-terminal domain (green) with the C-terminal domain (yellow) of the protease. B, shown is survival of Mtb in low pH. Mtb strains were plated after 3 (gray bars) and 6 (black bars) days of exposure to phosphate citrate buffer, pH 4.5, and cfu were quantified. Data are the means ± S.D. of triplicate cultures. C, survival of Mtb after exposure to hydrogen peroxide is shown. Mtb strains were plated after exposure to 8 mm H2O2 for 4 h (black bars). Data are means ± S.D. of triplicate cultures.