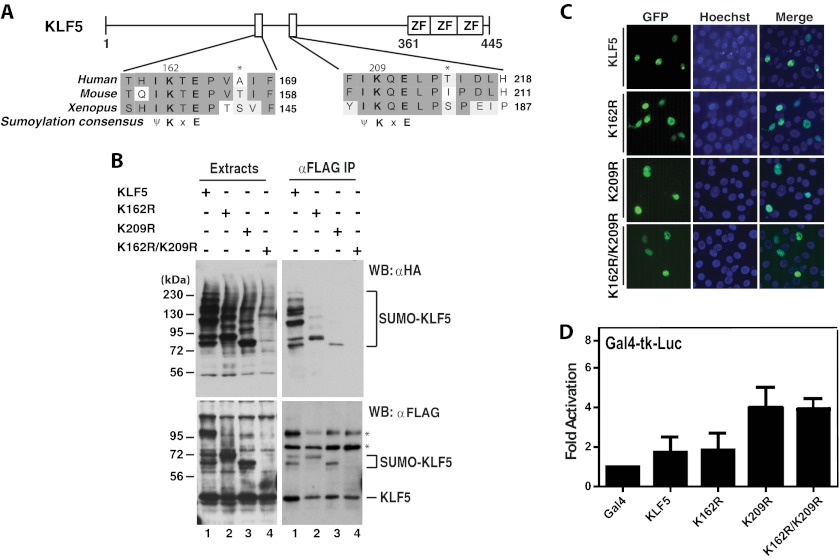
FIGURE 6.
KLF5 sumoylation and the effects on subcellular localization and transcription. A, domain organization of KLF5 illustrated with sequence alignment of two conserved sumoylation motifs and adjacent residues in human, mouse, and Xenopus KLF5 proteins. ZF, zinc finger. B, sumoylation assays. Expression plasmids for HA-SUMO2 and FLAG-tagged wild-type and mutant KLF5 were co-transfected into HEK293 cells as indicated. 48 h later, extracts were prepared for IP on anti-FLAG M2-agarose and immunoblotting with anti-HA and -FLAG antibodies. Asterisks denote nonspecific bands. WB, Western blot. C, subcellular localization of GFP-tagged wild-type and mutants of KLF5 and after transient transfection of the corresponding expression plasmids into HEK293 cells. Cells were fixed and incubated with Hoechst 33258 for fluorescence microscopy to detect GFP expression (green) and nuclei (blue). D, reporter gene assays. The Gal4-tk-Luc construct was transfected into HEK293 cells along with expression plasmids for expression of the Gal4 fusion proteins containing the Gal4 DNA-binding domain fused to the wild-type and point mutants of KLF5 as indicated. Luciferase activities were normalized to β-galactosidase activities expressed from CMV-β-Gal co-transfected as the internal control.