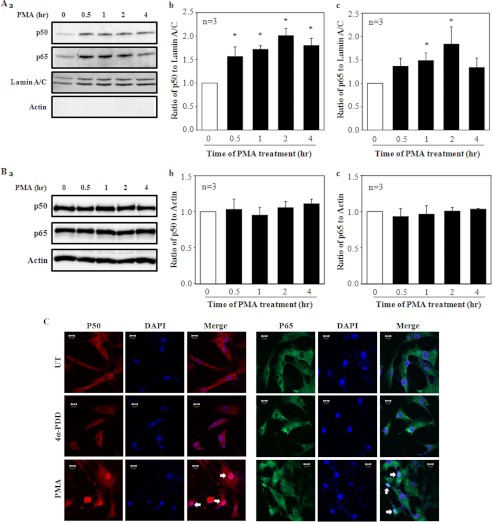
FIGURE 7.
Nuclear translocation of NF-κB in response to PMA treatment in human MCs. A and B, a Western blot shows expressions of p50 and p65 NF-κB subunits in the nuclear extracts (A) and whole cell lysates (B) in MCs with 1 μm PMA treatment for various time periods. Aa, shown are representative immunoblots of the nuclear extracts. Lamin A/C was used as a loading control of nuclear proteins. Actin was used to determine whether the nuclear extracts were contaminated by the cytoplasmic fractions. A, b and c, shown is quantification of nuclear p50 and p65 proteins by normalization to lamin A/C from experiments indicated in Aa. The value at time 0 of PMA treatment was considered as 1. * denotes p < 0.05, versus time 0. n indicates the number of independent experiments. Ba, representative shown are immunoblots of the whole cell lysates. Actin was used as a loading control. B, b and c, shown is quantification of p50 and p65 proteins by normalization to actin from experiments indicated in Ba. The value at time 0 of PMA treatment was considered as 1. n indicates the number of independent experiments. C, shown is immunofluorescence staining of p50 (red) and p65 (green) in MCs with and without PMA or 4α-PDD at 1 μm for 30 min. UT represents MCs without PMA and 4α-PDD treatments. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate the nuclear localization of p50 or p65.