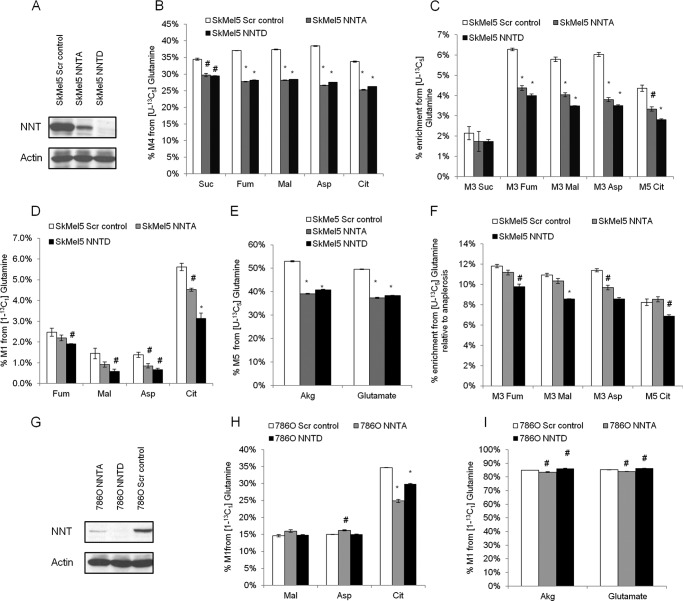
FIGURE 1.
Effect of NNT knockdown on glutamine catabolism. A, validation of NNT knockdown in SkMel5 cells. B–F, effect of NNT knockdown on glutamine metabolism in SkMel5 cells. B and C, contribution of glutamine oxidation (B) and reductive carboxylation (C) to the TCA cycle, from [U-13C5]glutamine. Scr control, scramble control; Suc, succinate; Fum, fumarate; Mal, malate; Asp, aspartate; Cit, citrate. D, contribution of reductive carboxylation to the TCA cycle using the [1-13C1]glutamine tracer. E, contribution of glutamine anaplerosis to α-ketoglutarate (Akg) formation. F, normalized contribution of reductive carboxylation in the panel of SkMel5 cells, from [U-13C5]glutamine. G, validation of NNT knockdown in 786-O cells. H, contribution of reductive carboxylation to the TCA cycle in NNT knockdown 786-O cells. I, contribution of glutamine anaplerosis to α-ketoglutarate (Akg) formation in 786-O cells.