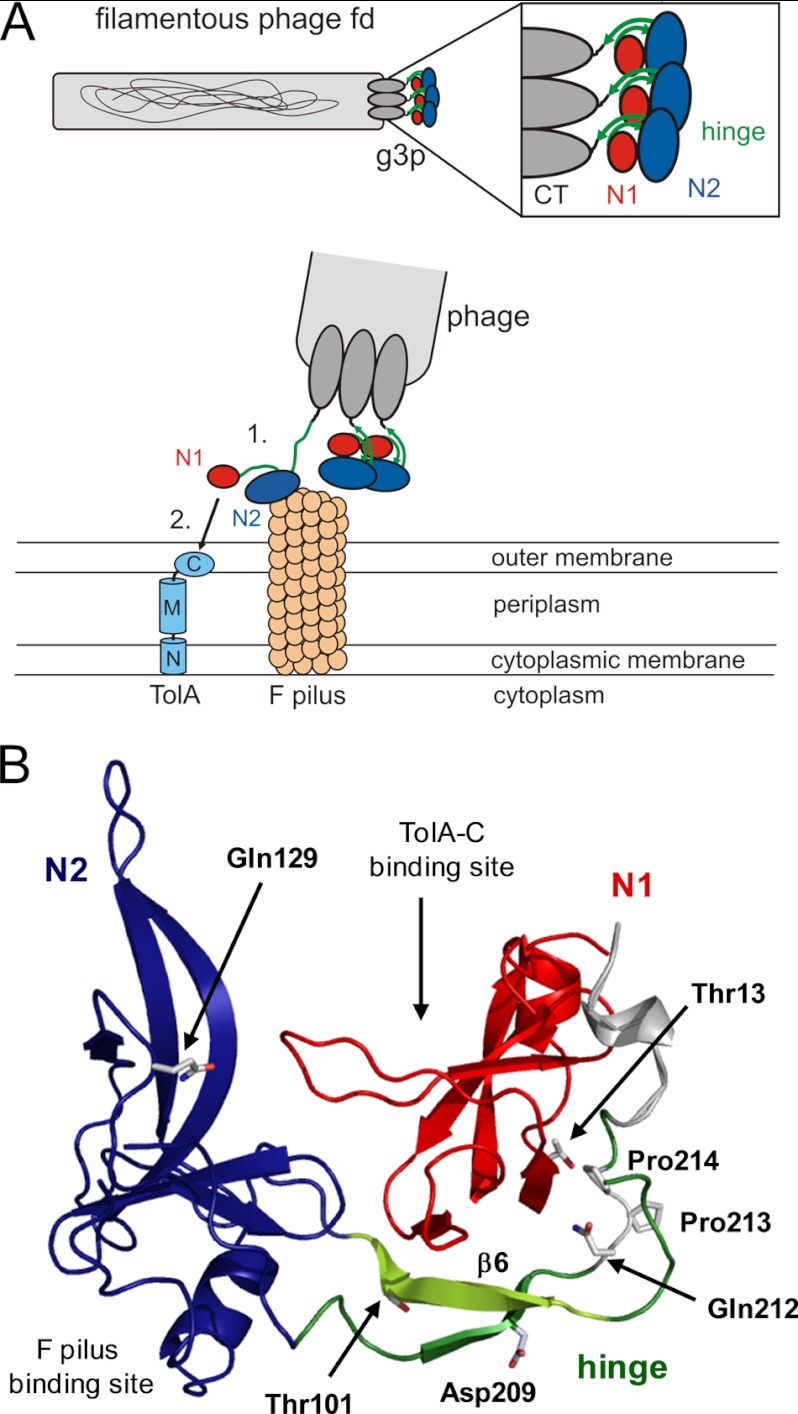
FIGURE 1.
Function of G3P during the phage infection process. A, top, arrangement of the domains of G3P at the pilus tip. Bottom, opening of G3P during infection and interaction of domain N2 (blue)) with the pilus (1), partial unfolding of the hinge subdomain (green), and binding of domain N1 (red) to the C-terminal domain of TolA (shown in light blue: N, M, and C, N-terminal, middle, and C-terminal domains, respectively, of TolA) (2). B, tertiary structure of wild-type G3P showing the amino acids that were substituted in this work. Domain coloring is as in panel A. The binding sites for the F pilus and the C-terminal domain of TolA are indicated. Strand β6 of the hinge, which is deleted in G3P Δβ6, is depicted in light green. Positions 13, 101, 129, and 209 of the stabilizing substitutions in G3P IIHY as well as Gln-212, cis-Pro-213 and Pro-214 are shown in stick representation. The figure was prepared by using PyMOL (31) and the Protein Data Bank (PDB) file 2g3p (5).