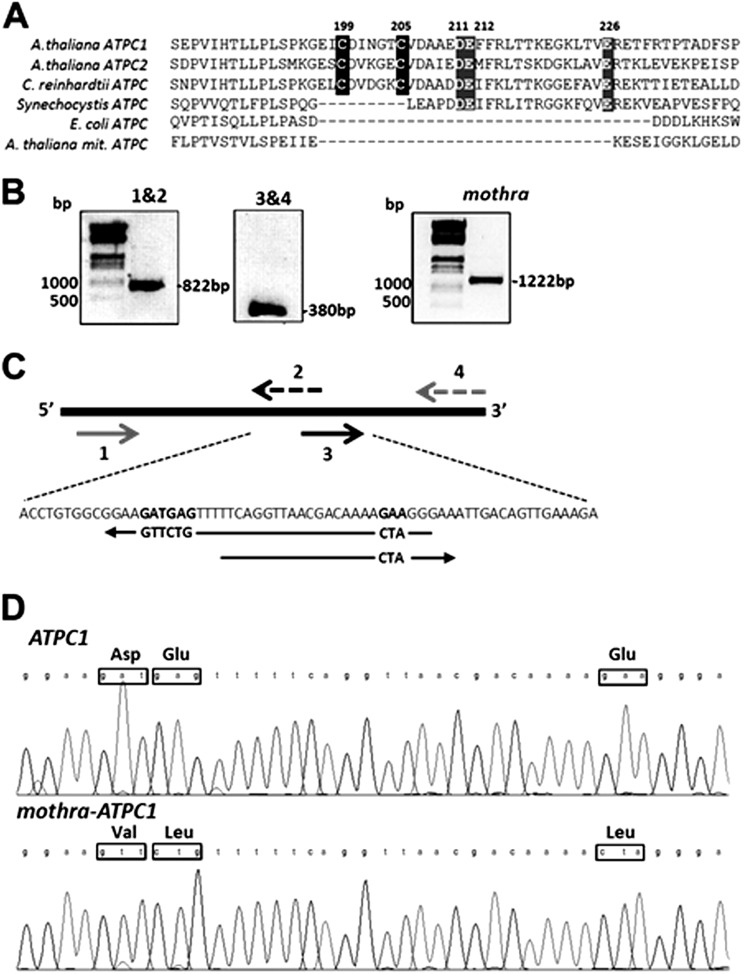
FIGURE 1.
A, alignment of partial protein sequences of γ subunits from different sources, chloroplast ATPC1 and ATPC2 from A. thaliana, ATPC of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Synechocystis, Escherichia coli, and mitochondrial ATPC subunit of A. thaliana. The cysteine residues (black background) involved the redox modulation of plant and algal plastid ATP synthase, and the highly conserved acidic residues are indicated by a gray background. B, oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of the ATPC1 gene. SmaI restriction-sited forward primer and modified ATPC1 reverse primer (1 and 2) amplified a fragment of 822 bp; modified ATPC1 forward primer and XbaI restriction-sited reverse primer (3 and 4) amplified a fragment of 380 bp. C, details of the mutagenesis strategy. D, sequence analysis of wild-type and mutant γ subunit.