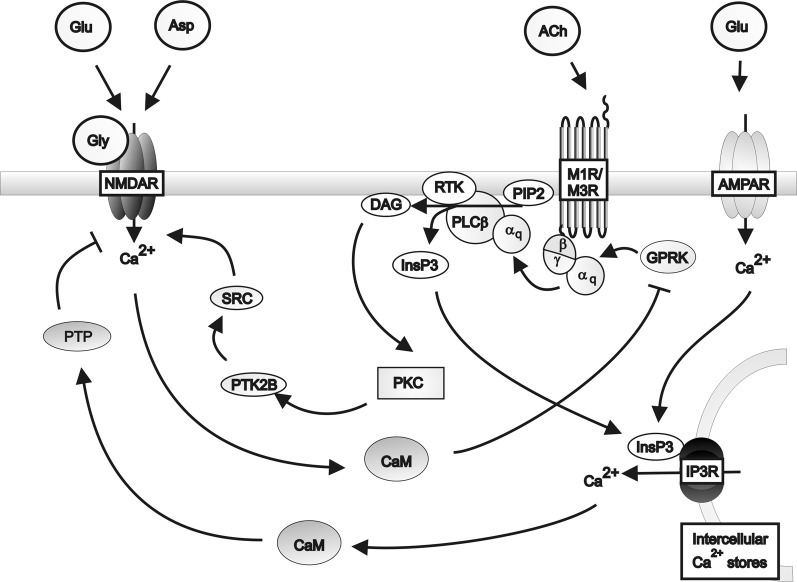
Figure 2.
A schematic diagram of the regulation of NMDA receptor activity by Gq protein-coupled muscarinic receptors in the hippocampus. Muscarinic receptors inhibit NMDA receptor activity via the activation of protein tyrosine phosphatase mediated by inositol triphosphate receptor pathways in conjunction with AMPA receptor induced calcium release from intracellular calcium stores. Muscarinic receptors can stimulate NMDA receptor activity via the activation of Src family tyrosine kinase in response to PKC signaling. Activation of the NMDA receptor by glutamate or aspartate and the co-agonist glycine, in turn inhibits muscarinic receptor activity via calmodulin inhibition of G protein coupled receptor kinases. αq: Gqα subunit; β: Gβ subunit; γ: Gγ subunit; ACh: Acetylcholine; AMPAR; AMPA receptor; Asp: Aspartate; CaM: Calmodulin DAG: Diacyl glycerol; Glu: Glutamate; Gly: Glycine; GPRK: G protein coupled receptor kinase; InsP3: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; IP3R: Inositol triphosphate receptor; M1R: Muscarinic M1 receptor; M3R: Muscarinic M3 receptor; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; NMDAR: NMDA receptor; PLCβ: Phospholipase C β; PIP2; Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PKC: Phosphokinase C; PTK2B: Protein tyrosine kinase 2β; PTP: Protein tyrosine phosphatase; RTK: Tyrosine kinase receptor; SRC: Src family tyrosine kinase.