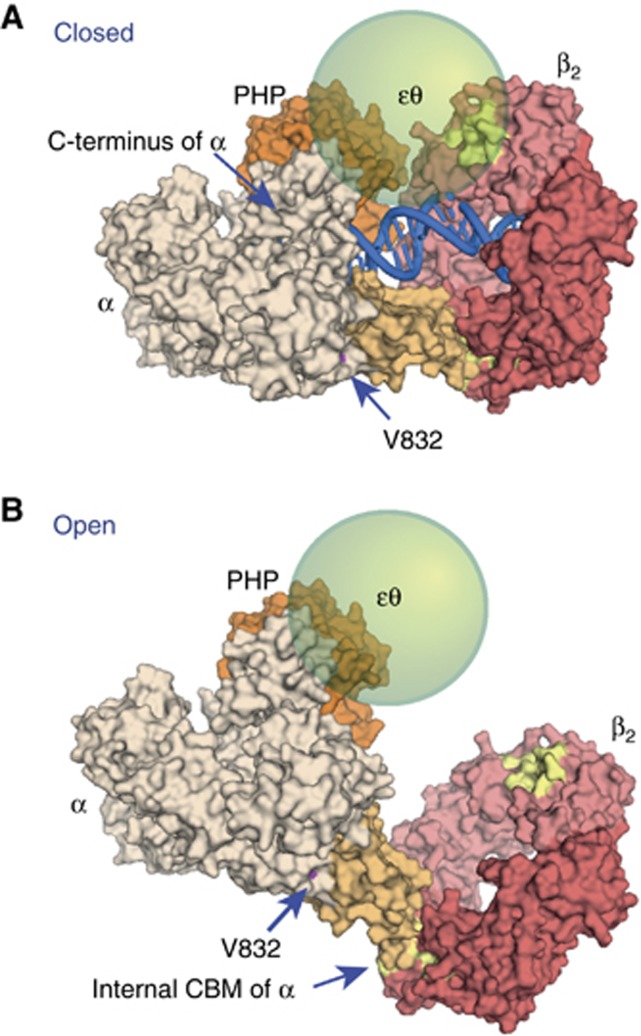
Figure 7.
Structural models of α–β2 complexes. (A) Binding of E. coli β2 to the β-binding domain of Taq α (tan) in the ‘closed’ DNA-bound form, modelled on the structure of the ternary complex of Taq α with DNA and dNTP (as described in Wing et al, 2008). Space exists to accommodate εθ between the ε-binding site in β2 (yellow) and the PHP domain of α (orange), spanned by residues 188–210 of ε that remain flexible in the αεθ complex (Ozawa et al, 2008). The location of Leu888 in Taq α (Val832 in E. coli) is shown. (B) Model of the ‘open’ complex (DNA not shown) derived by rigid body transformation of the β-binding domain–β2 moiety in (A) to superimpose on the β-binding domain in the structure of Taq α without DNA (Bailey et al, 2006). Figures were produced using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific, San Carlos CA).