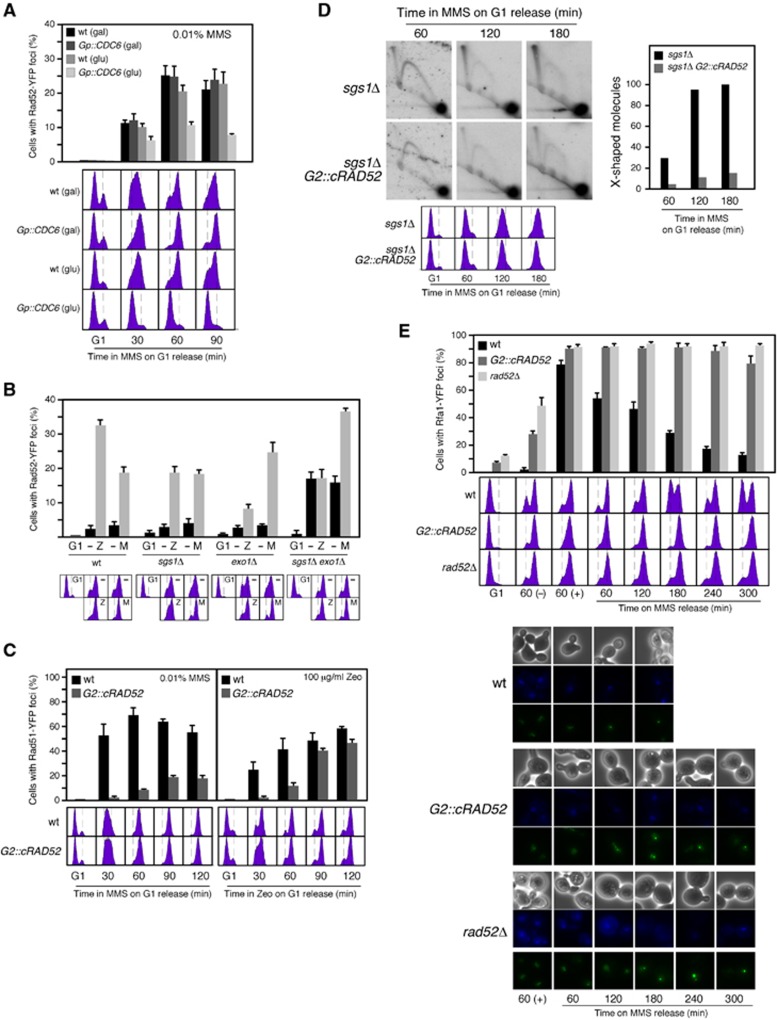
Figure 3.
Rad51 fork recruitment is a prerequisite for MMS-induced HR repair. (A) DNA replication is required for MMS-induced Rad52-YFP foci. Rad52 foci accumulation in wild-type and Gp::CDC6 cells transformed with pWJ1344 (RAD52-YFP), synchronized in G1 as shown in Figure 1F, and released in YP glucose with 0.01% MMS. (B) Sgs1 and Exo1 are required for zeocin-induced, but not for MMS-induced HR foci. Rad52 foci accumulation in wild-type, sgs1Δ, exo1Δ, and sgs1Δ exo1Δ cells transformed with pWJ1344 (RAD52-YFP), synchronized in G1, and released in the presence of 0.01% MMS (M) or 100 μg/ml zeocin (Z) for 90 and 120 min, respectively. (C) Rad52 expression during S phase is required for MMS-induced, but not for zeocin-induced HR foci. Rad51 foci accumulation in YFP-RAD51 and G2::cRAD52 YFP-RAD51 cells transformed with pWJ1278 (RAD51), synchronized in G1, and released in the presence of 0.01% MMS (left panel) or 100 μg/ml zeocin (right panel). The average and s.e.m. are shown. (D) Rad52 expression during S phase is required for MMS-induced SCJs. 2D gel analysis of X-shaped molecules in sgs1Δ and sgs1Δ G2::cRAD52 cells synchronized in G1 and released in the presence of 0.033% MMS. The amount of X-shaped molecules relative to the total amount of molecules, taken the highest value as 100, is shown. The experiment was repeated with similar results. (E) Rad52 expression during S phase is required for ssDNA gap repair. RPA foci accumulation and FACS analysis in RFA1-YFP1, RFA1-YFP1 G2::cRAD52 and RFA1-YFP1 rad52Δ cells synchronized in G1, released in 0.01% MMS for 1 h, treated with 2.5% sodium thiosulphate to inactivate the MMS, washed and incubated in fresh medium for different times. Bright field, DAPI fluorescence, and Rfa1-YFP foci of selected cells are shown.