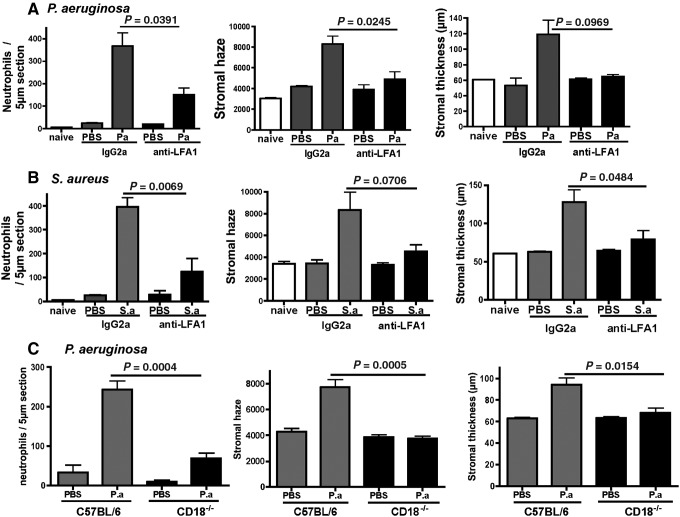
FIG. 1.
Effect of blocking lymphocyte functional antigen-1 (LFA-1) on Pseudomonas aeruginosa- and Staphylococcus aureus-induced corneal inflammation. C57BL/6 mice were treated i.p. with anti-LFA-1 or control rat IgG2a, and corneal inflammation was induced by tobramycin-killed P. aeruginosa (A) or S. aureus (B) in the presence of a contact lens punch. (C) Corneas of CD18−/− and C57BL/6 mice were abraded, and treated with killed P. aeruginosa. After 24 h, corneal thickness and haze were quantified by Confoscan analysis, and neutrophil infiltration to the corneal stroma was determined by direct counting of immunostained corneal sections. Data are mean±SD of 5 mice per group, and are representative of 2 repeat experiments for each organism.