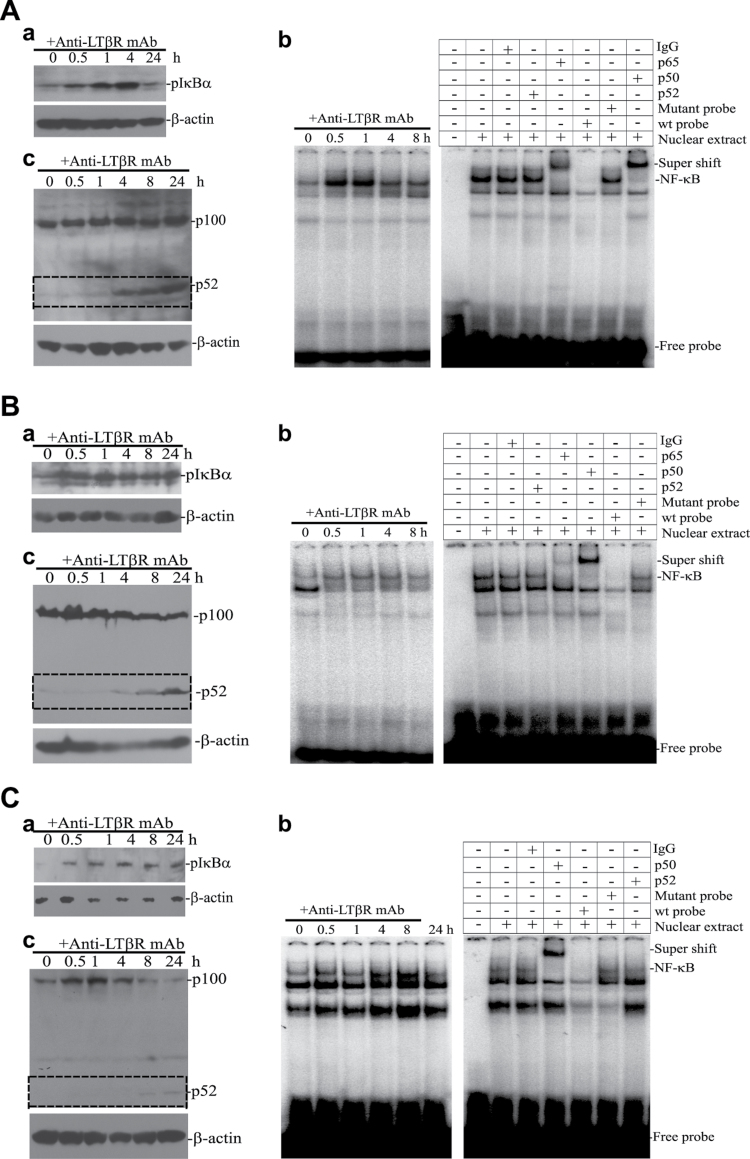
Fig. 4.
LTβR agonist mAb induces both canonical and alternate NF-κB activation in human cancer cells. Human colon carcinoma (HT29, A), mammary carcinoma (MCF-7, B) and STS (MPNST724, C) cells were cultured in the presence of BS-1 and analyzed for NF-κB activation. (a) Western blot analysis of IκBα activation (pIκBα). Tumor cells were incubated with BS-1 for the indicated time and analyzed with pIκBα-specific antibody. β-Actin was used as loading controls. (b) EMSA of canonical NF-κB activation kinetics. Tumor cells were treated with BS-1 for the indicated times and nuclear extracts were prepared. Nuclear extracts were incubated with NF-κB DNA probe and analyzed with 6% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Right panel: specificity control of EMSA. Nuclear extracts were prepared from BS-1-treated cells [30min for HT29 cells (A), 60min for MCF-7 cells (B) and 4h for MPNST724 cells (C), respectively] and incubated with 32P-labelled NF-κB probe in the presence of IgG, p52, p65, p50, excess cold NF-κB probe and excess cold mutant NF-κB probe. The DNA–protein complexes were analyzed by 6% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The canonical NF-κB (NF-κB1) complex is indicated. (c) Western blot analysis of alternate NF-κB activation. Tumor cells were incubated with BS-1 for the indicated times and analyzed with p100/p52-specific antibody. β-Actin was used as loading controls.