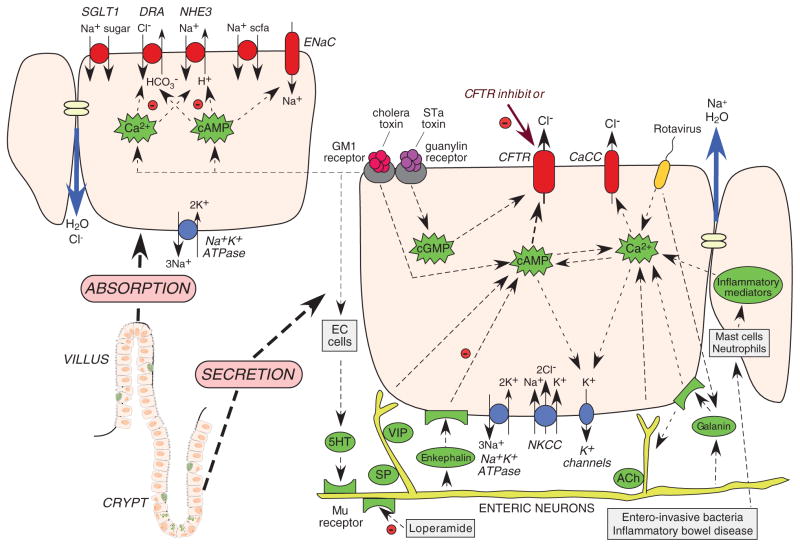
Figure 1.
Intestinal fluid transporting mechanisms. Lower left: crypt–villus unit in the small intestine, comprising basal crypt stem cells, enterocytes, enterochromaffin cells (EC cells), and goblet cells. Right: crypt secretory cell with luminal (top) and basal (bottom) transporters, ion channels, and second messengers. Left: villus absorptive cell with luminal (top) and basal (bottom) transporters. cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; CaCC, Ca2+-activated Cl− channel; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; STa, heat-stable.