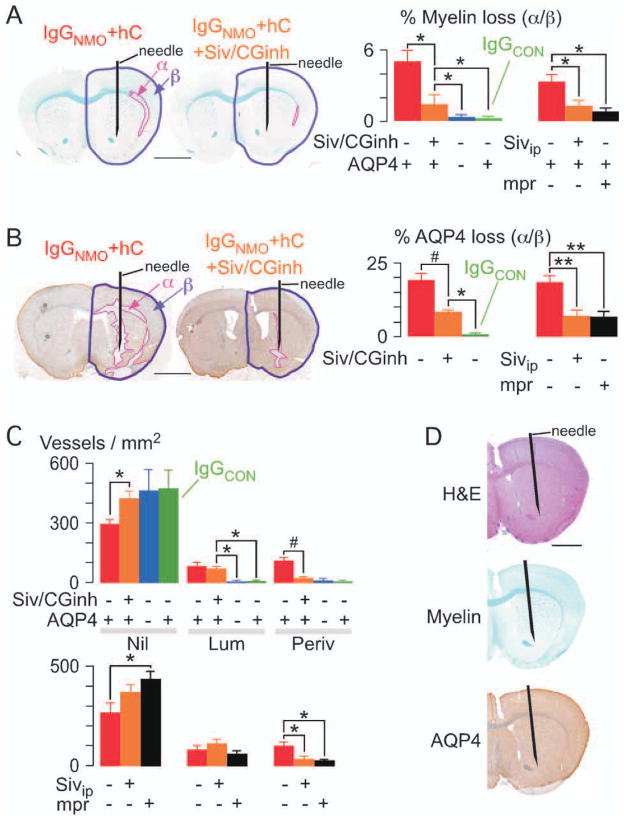
FIGURE 4.
Neutrophil protease inhibitors reduce brain damage at 24 hours after IgGNMO+hC injection. (A) LFB, and (B) AQP4 immunostain. (Left) Brain injected with IgGNMO+hC alone (IgGNMO+hC) or with Sivelestat and cathepsin G inhibitor I (IgGNMO+hC+Siv/CGinh). (Right) % area-α/area-β (A) loss of myelin and (B) loss of AQP4 after IgGNMO+hC (6 mice, red), IgGNMO+hC+Siv/CGinh (6 mice, orange), IgGNMO+hC (5 AQP4 null mice, blue), or IgGCON+hC (5 mice, green). (Far Right) % area-α/area-β (A) loss of myelin and (B) loss of AQP4 after injecting IgGNMO+hC without (6 mice, red) vs with i.p. Sivelestat (6 mice, orange) vs with i.p. methylprednisolone (5 mice, black). (C) Number of Nil, Lum, and Periv vessels/mm2. (Top) IgGNMO+hC (6 mice, red), IgGNMO+hC+Siv/CGinh (6 mice, orange), IgGNMO+hC (5 AQP4 null mice, blue), or IgGCON+hC (5 mice, green). (Bottom) IgGNMO+hC without (6 mice, red) vs with i.p. Sivelestat (6 mice, orange) vs. with i.p. methylprednisolone (5 mice, black). (D) Brain at 24 hours after intracerebral injection of NE and Cath G: H&E (top), LFB (middle), AQP4 immunostain (bottom). Mean ± standard error. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, #p < 0.005 vs IgGNMO+hC+Siv/CGinh or +Sivip. Bar = 2mm (A, B, D).