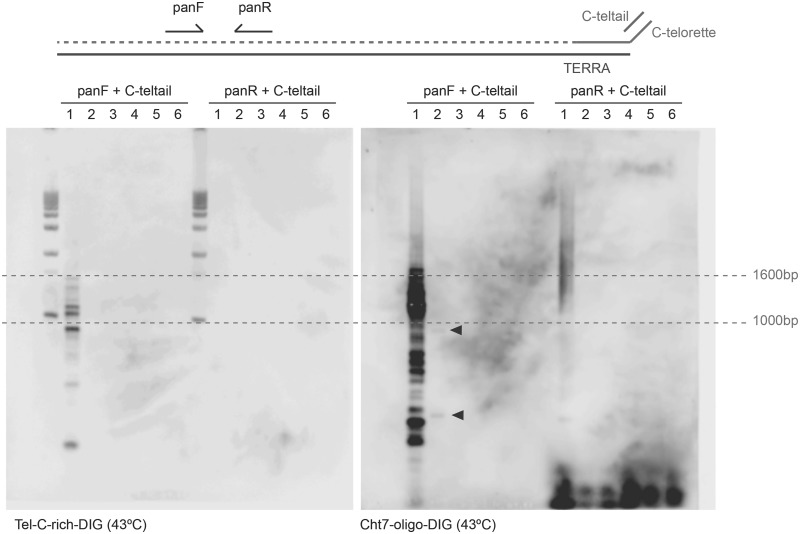
Figure 6.
Telomere repeats and the Cht7 minisatellite are physically linked on gorilla chromosomes and are co-transcribed. A PCR approach was adapted to determine whether Cht7 and telomeric sequences were physically linked and co-transcribed. A telomeric C-rich primer, ending with a unique 3′-end (C-telorette) was used to reverse transcribe total gorilla RNA (top). The unique sequence (C-teltail) was used to prime PCR reactions in combination with primers specific to Cht7-sequence, either in the sense (panF) or in the antisense (panR) orientation. PCR products were separated in a 1% agarose gel and hybridized with either digoxigenin-labeled telomeric C-rich probes (bottom left) or Cht7-oligo (bottom right). PCR templates included: lane 1: genomic DNA; lane 2: cDNA transcribed with C-telorette3; lane 3: same RNA sample treated as in 2 but leaving out the reverse transcriptase (RT); lane 4: same as in 3 but treated with DNAse I; lane 5: same as in 3 but treated with RNase I; and lane 6: RT reaction with no RNA. Both the telomeric and the Cht7 probes revealed amplified products from genomic DNA exclusively obtained with the combination C-teltail/panF, indicating proximity of both sequences and allowing orienting the minisatellite repeats with regard to the telomeric sequences. On the other hand, the Cht7 probe reveals rare molecules (arrows) amplified using the same couple of primers and the C-telorette cDNA, suggesting the presence of RNA molecules carrying both telomere and Cht7 repeats.