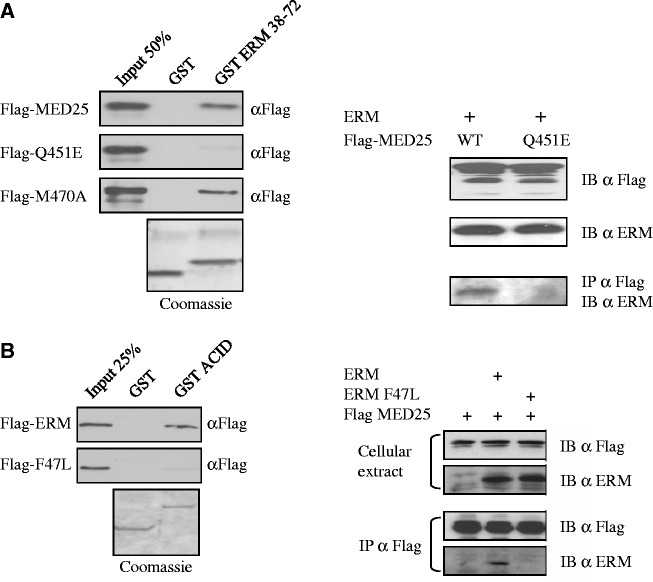
Figure 2.
Effect of mutations in the ERM/MED25 interface. (A) Mutation of Q451 of MED25 severely reduces its ability to bind to ERM. (Left) GST ERM 38–72 was used to analyse the binding to full-length Flag-MED25 WT and point mutants Q451E and M470A. Q451E shows weak binding to ERM 38–72. Binding was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Flag. An SDS gel stained with Coomassie showing the expression of the GST fusion proteins is shown. (Right) Wild-type Flag-MED25 or MED25 with a Q451E mutation were examined for their ability to interact with ERM in co-immunoprecipitation experiments. RK13 cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors and cellular extracts were IP α Flag and IB α Flag. Expression of Flag-MED25, Flag-MED25 Q451E and ERM are shown in the top two panels. (B) Mutation of F47 of ERM abolishes the recruitment of MED25. (Left) GST MED25 ACID domain was examined for its ability to interact in vitro with ERM wild type or ERM F47L mutant. (Right) The ability of Flag-MED25 to interact with ERM wild type and with ERM F47L mutant was analysed in co-immunoprecipitation experiments. Cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors and cellular extracts were IP α Flag and IB α Flag or IB α ERM (IB). Expression of Flag-MED25, ERM and ERM F47L are shown in the top panel (cellular extract).