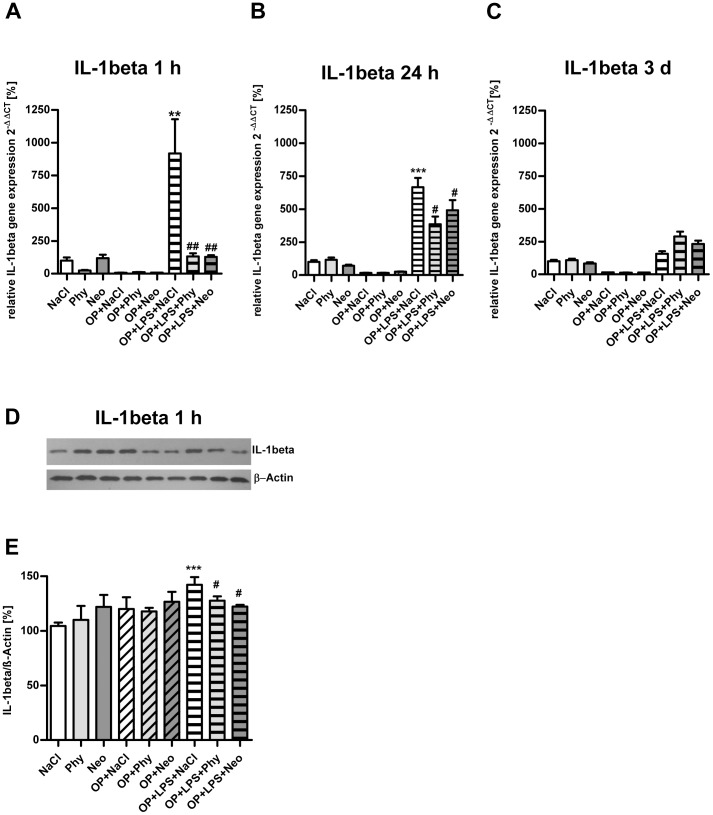
Figure 1. Physostigmine and neostigmine reduce surgery combined with LPS-induced IL-1beta expression in the cortex.
IL-1beta expression was measured by quantitative Real-Time PCR in cortex samples extracted 1, 24, and 72 h postintervention (A–C). Also, IL-1beta expression was detected by western blot analysis in cortex samples extracted 1 h postintervention (D–E). Surgery combined with LPS-treatment resulted in an increased gene expression of IL-1beta after 1 and 24 h, which was decreased by physostigmine and neostigmine administration. Results of Real-Time PCR quantification are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 8 per group). Data are normalized to levels of saline treated rats (Control = 100%; bars represent mean ± SEM, n = 8 per group). Blots are representative of a series of three blots. The densitometric data represent the ratio of the IL-1beta band to the corresponding β-actin band density. ***P<0.001 and **P<0.01 represent the difference between LPS and saline treated groups. ##P<0.01 and #P<0.05 represent the difference between LPS and physostigmine or neostigmine treated groups.