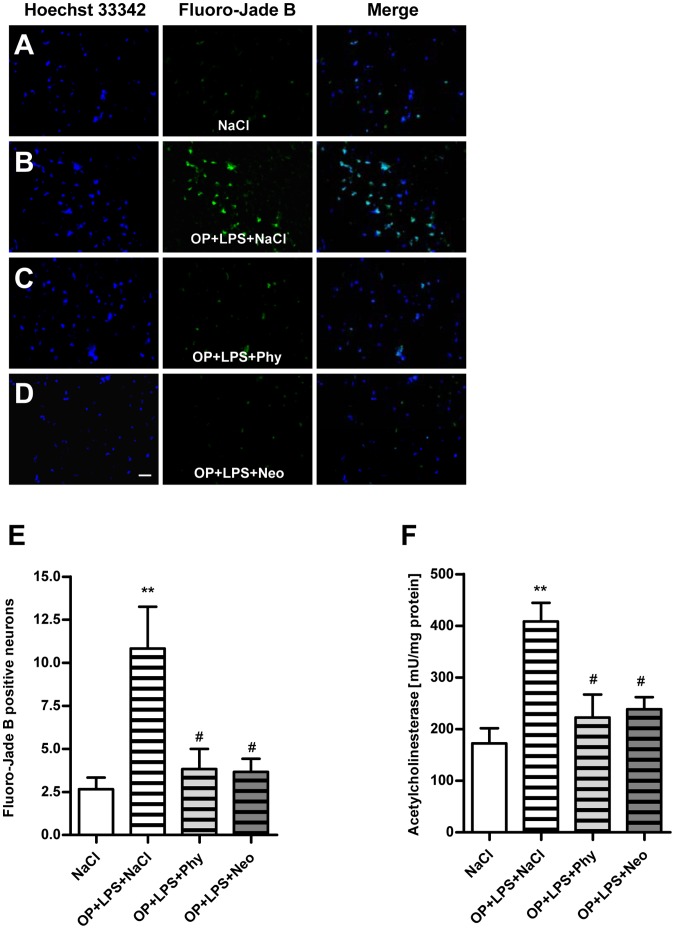
Figure 5. Physostigmine and neostigmine reduce surgery combined with LPS-induced neurodegeneration and activity of acetylcholinesterase in the cortex.
Representative photomicrographs (original magnification X200) of Hoechst 33342 (left panel) and Fluoro-Jade B (right panel) staining from the cortex (Scale bar = 20 µm) of adult rats which were treated with saline (A), surgery combined with LPS-treatment+saline (B), surgery combined with LPS-treatment+physostigmine (C) or surgery combined with LPS-treatment+neostigmine (D). (E) Comparison of the number of Fluoro-Jade B-positive cells from the cortex of adult rats. (F) Activity of acetylcholinesterase in the cortex after 1 h. Surgery combined with LPS-treatment triggered the number of degenerated neurons and the activity of acetylcholinesterase in the cortex after 1 h. Physostigmine and neostigmine led to significantly reduced neuronal damage and activity of acetylcholinesterase. Number of Fluoro-Jade B-positive cells are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 5–6 per group). **P<0.01 represents the difference between surgery combined with LPS-treatment and saline treated groups. #P<0.05 represents the difference between surgery together with LPS-treatment and in combination with physostigmine or neostigmine treated groups.