Figure 6. A schematic drawing showing the underlying mechanism of micturition inhibition by EM2-containing bladder afferent terminals onto the MOR-expressing PPNs in the SPN.
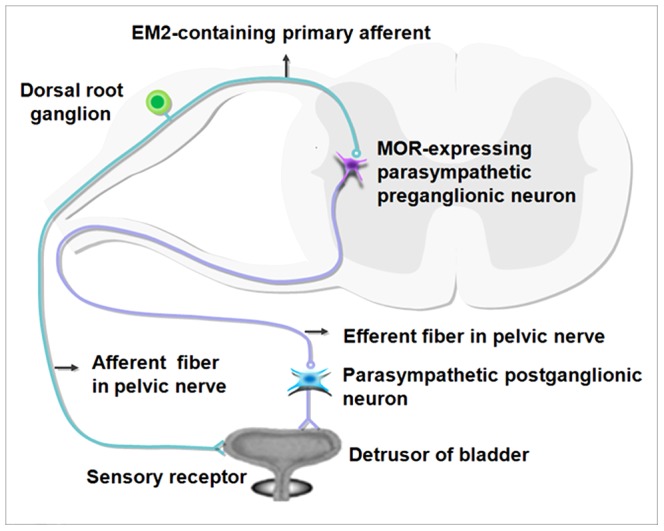
Sensory information from the bladder receptor is directly transmitted to the MOR-expressing PPNs via EM2-containing primary afferent fibers. These EM2-containing fibers exert inhibitory effects onto the MOR-expressing PPNs in the SPN via synaptic connections, resulting in an attenuation of the excitatory effects of the efferent fibers originating from the PPNs onto the parasympathetic postganglionic neurons in the pelvic ganglia. This attenuation affects the micturition reflex and results in urinary retention.
