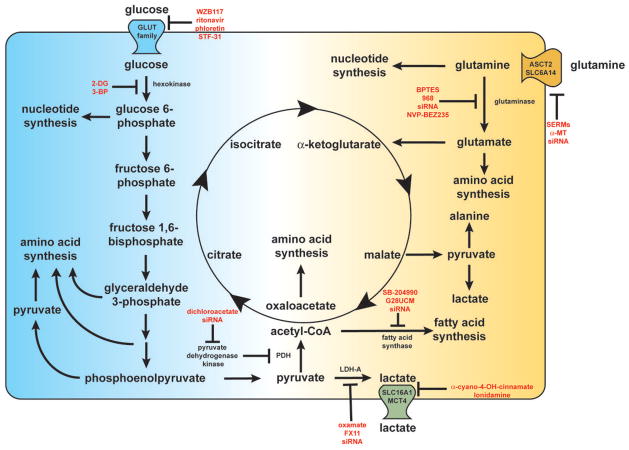
Figure 1.
A wide range of metabolic components support the cancerous phenotype. Glucose and glutamine are metabolized into critical intermediates necessary for cellular growth, such as amino acids, nucleotides, and fatty acids. The metabolic inhibitors discussed within this manuscript are listed in red near their target of inhibition. Disruption of these metabolic networks can reduce drug resistance and render cancer cells more susceptible to current therapeutic regimens.