Fig. 2.
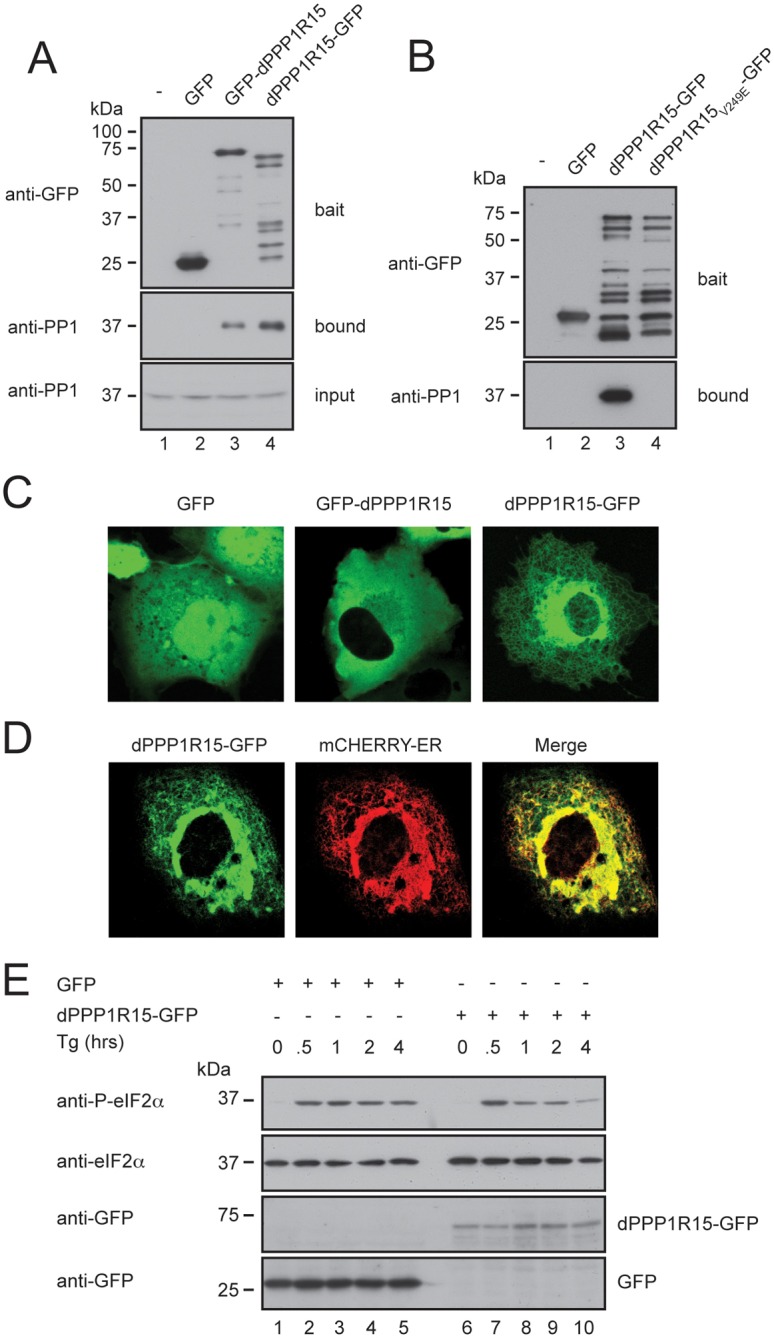
dPPP1R15 and PP1 form an ER-associated eIF2α phosphatase when expressed in mammalian cells. (A) Immunoblots of GFP-Trap affinity purification of lysates from HEK 293T cells expressing no transgene (lane 1), GFP alone (lane 2), GFP-dPPP1R15 (lane 3) or dPPP1R15-GFP (lane 4). Lysates were subjected to GFP-Trap affinity-purification and analysed by 10% (w/v) SDS-PAGE and probed for GFP and PP1. Input samples were probed for PP1. (B) Immunoblots of GFP-Trap affinity purification of lysates from HEK293T cells expressing no transgene (lane 1), GFP alone (lane 2), dPPP1R15-GFP (lane 3) or dPPP1R15V249E-GFP (lane 4). Lysates were subjected to GFP-Trap affinity-purification and analysed by 10% (w/v) SDS-PAGE and probed for GFP and PP1. Note large number of degradation products with C-terminally tagged dPPP1R15, as also seen in A, lane 4. (C) Representative fluorescence confocal images of COS-7 cells expressing GFP, GFP-dPPP1R15 or dPPP1R15-GFP. (D) Representative fluorescence confocal image of a COS-7 cell expressing dPPP1R15-GFP and the ER marker ER-mCherry. (E) Immunoblot of lysates from HEK 293T cells expressing either dPPP1R15-GFP (lanes 6–10) or GFP alone (lanes 1–5), followed by treatment with 500 nM thapsigargin for the indicated times. Lysates were analysed by 10% (w/v) SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot for phosphorylation of eIF2α (P-eIF2α), total eIF2α and GFP.
