Fig. 8.
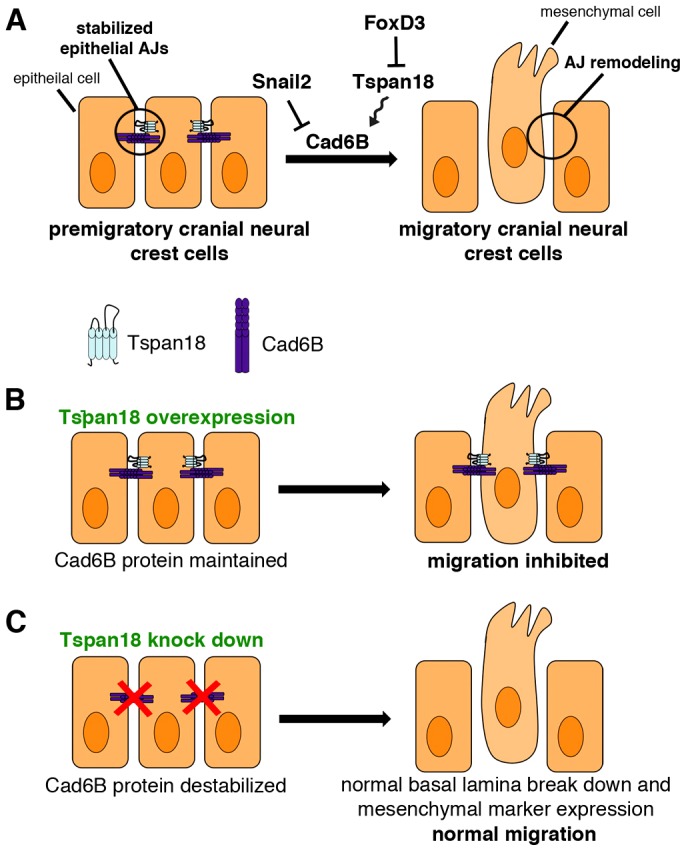
Role of Tspan18 in cranial neural crest EMT. (A) Epithelial, premigratory cranial neural crest cells are tightly joined by Tspan18-stabilized, Cad6B-containing adherens junctions (AJs). During EMT, neural crest cells transcriptionally downregulate Cad6B via Snail2 and post-translationally destabilize Cad6B by FoxD3-dependent downregulation of Tspan18 to remodel their AJs in preparation for migration. (B) Evidence for the role of Tspan18. Sustained expression of Tspan18 maintains Cad6B protein and promotes Cad6B-dependent AJs, inhibiting neural crest migration. (C) By contrast, loss of Tspan18 results in premature downregulation of Cad6B protein but normal cranial neural crest migration, presumably reflecting a need for coordinated transcriptional and post-translational regulation of Cad6B and temporally normal delamination and expression of mesenchymal markers. Thus, loss of Tspan18 is necessary, but not sufficient, for cranial neural crest migration.
