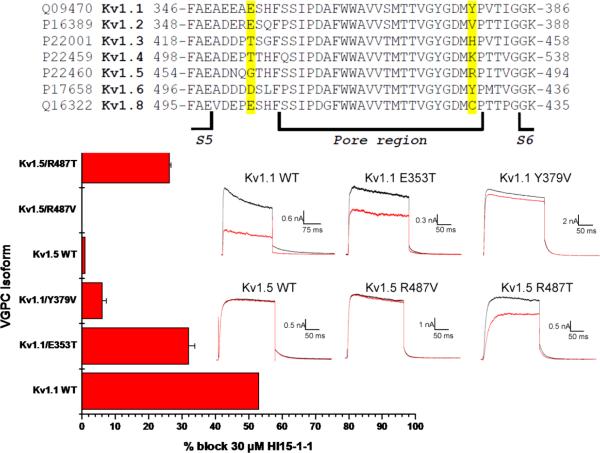
Fig. 6.
Multiple sequence alignment of the pore region of the tested Shaker-related VGPCs. The amino acids considered most important for the selectivity of Hl15-1-1 towards Kv1.1 and Kv1.6 are highlighted in yellow. Those residues have been mutated resulting in the channels Kv1.1 E353T, Kv1.1 Y379V, Kv1.5 R487V and Kv1.5 R487T. The bar diagram shows the inhibition caused by 30 μM Hl15-1-1 on the wildtype (WT) and mutated channels (mean ± SEM). Current recordings of Kv1.1 and Kv1.5 wildtype and mutant channels were elicited by a depolarizing step to +10 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV followed by a repolarization to −50 mV. Raw current traces are shown in control (black) and after application of 30 μM Hl15-1-1 (red). Scale bars are given as inset.