Fig. 4.
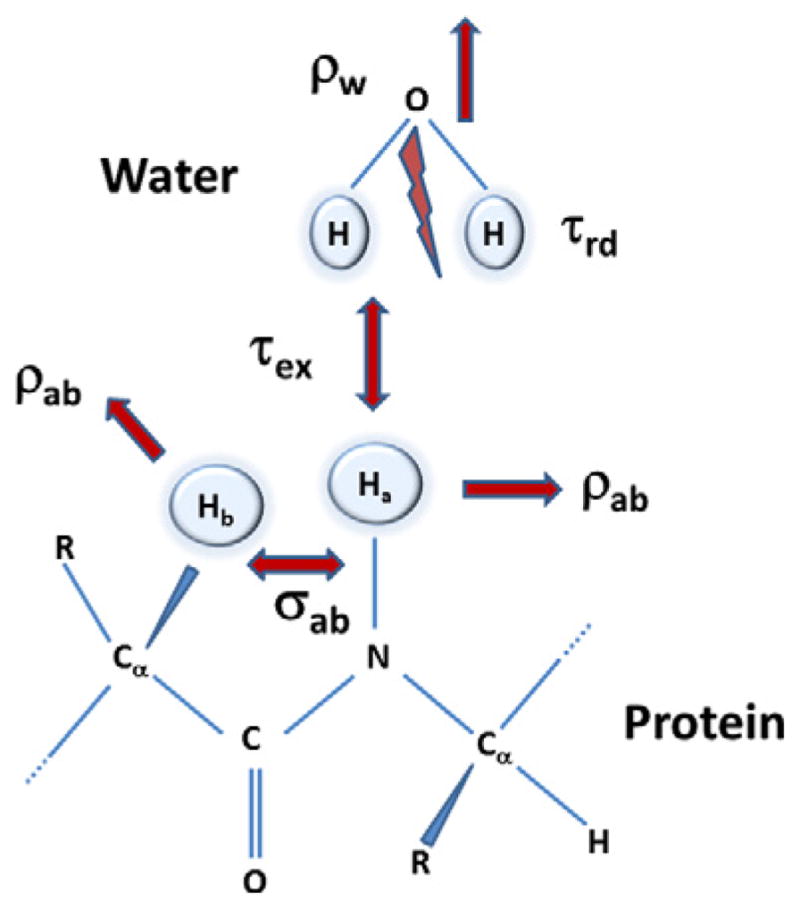
Schematic representation of the spin system considered in developing a system of equations to consider radiation damping effects of the water as well as its chemical exchange with a labile proton in a protein. Spins ‘a’ and ‘b’ are the amide proton and a proton in a protein, respectively. Water and the protein spins have their respective relaxation mechanism given by ρw and by the self-relaxation (ρab) and cross relaxation rates (σab). The radiation damping of the water spins are characterized by a time constant τrd and the intermolecular exchange between the water and the amide proton is given by τex. The protein concentration is considered too low to have any radiation damping effects of its own.
