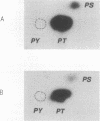
Abstract
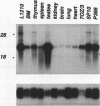
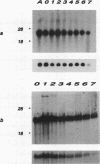
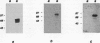
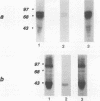
A novel protein kinase, the Esk kinase, has been isolated from an embryonal carcinoma (EC) cell line by using an expression cloning strategy. Sequence analysis of two independent cDNA clones (2.97 and 2.85 kb) suggested the presence of two Esk isoforms in EC cells. The esk-1 cDNA sequence predicted an 857-amino-acid protein kinase with a putative membrane-spanning domain, while the esk-2 cDNA predicted an 831-amino-acid kinase which lacked this domain. In adult mouse cells, esk mRNA levels were highest in tissues possessing a high proliferation rate or a sizeable stem cell compartment, suggesting that the Esk kinase may play some role in the control of cell proliferation or differentiation. As anticipated from the screening procedure, bacterial expression of the Esk kinase reacted with antiphosphotyrosine antibodies on immunoblots. Furthermore, in in vitro kinase assays, the Esk kinase was shown to phosphorylate both itself and the exogenous substrate myelin basic protein on serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues, confirming that the Esk kinase is a novel member of the serine/threonine/tyrosine family of protein kinases.
Full text
PDF




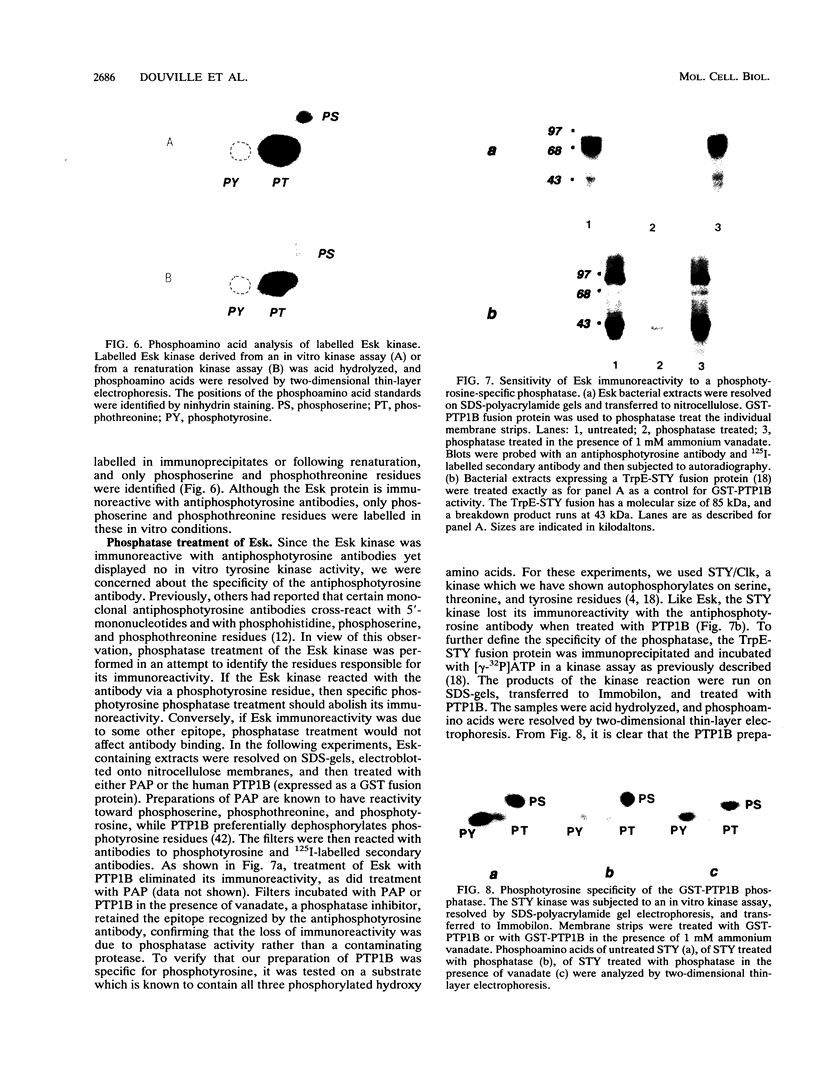
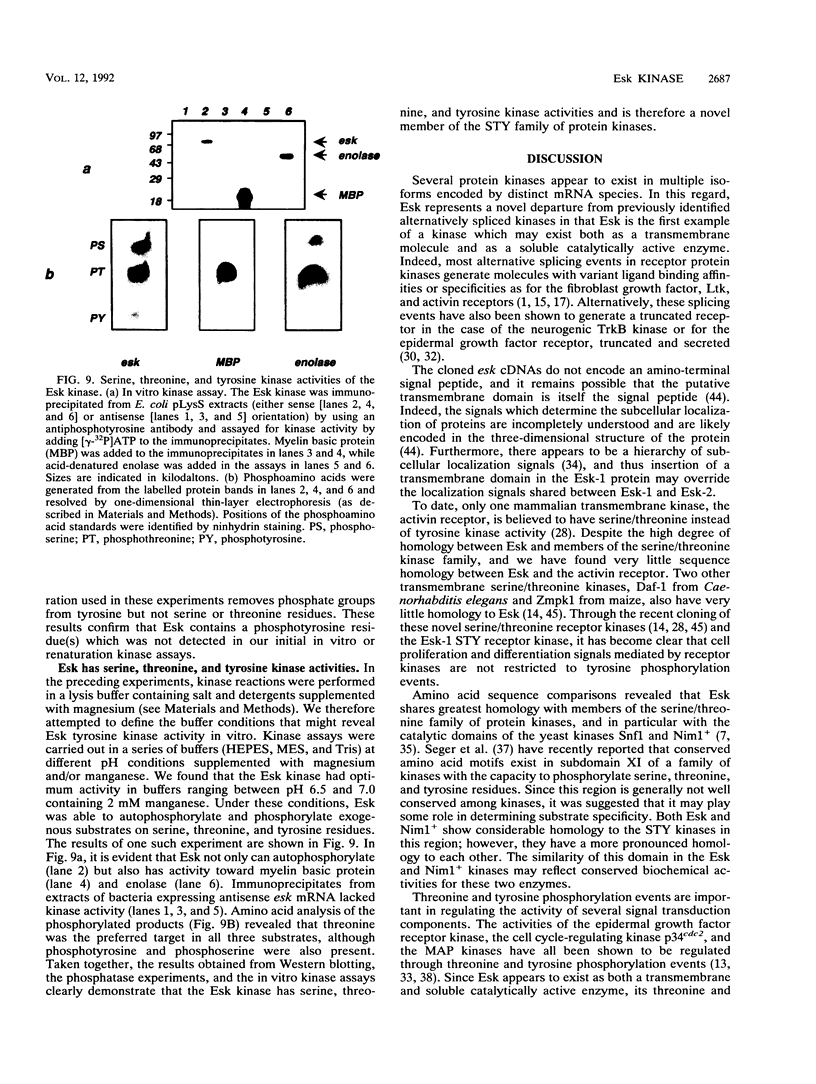


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Novel activin receptors: distinct genes and alternative mRNA splicing generate a repertoire of serine/threonine kinase receptors. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90209-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. C., Mahadevan L. C., Colledge W. H., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Sargent M. G., Foulkes J. G. Abelson-transformed fibroblasts contain nuclear phosphotyrosyl-proteins which preferentially bind to murine DNA. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):552–554. doi: 10.1038/325552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Letwin K., Tannock L., Bernstein A., Pawson T. A mammalian protein kinase with potential for serine/threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation is related to cell cycle regulators. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):317–325. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards A., de la Monte S. M. The ltk receptor tyrosine kinase is expressed in pre-B lymphocytes and cerebral neurons and uses a non-AUG translational initiator. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2279–2287. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhut S., Chaplin T., Young B. D. Normal c-abl gene protein--a nuclear component. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1459–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. M., Arquint M., Braun P. E., Roder J. C., Dunn R. J., Pawson T., Bell J. C. Myelin-associated glycoprotein, a cell adhesion molecule of oligodendrocytes, is phosphorylated in brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2655–2658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Thrombin stimulates the activities of multiple previously unidentified protein kinases in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20723–20729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Eisen H. N. Characterization and use of monoclonal antibodies for isolation of phosphotyrosyl proteins from retrovirus-transformed cells and growth factor-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1343–1352. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgi L. L., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. daf-1, a C. elegans gene controlling dauer larva development, encodes a novel receptor protein kinase. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90475-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase V. H., Snijders A. J., Cooke S. M., Teng M. N., Kaul D., Le Beau M. M., Bruns G. A., Bernards A. Alternatively spliced ltk mRNA in neurons predicts a receptor with a larger putative extracellular domain. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2319–2325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. Z., Kan M. K., McKeehan K., McBride G., Adams P., McKeehan W. L. Fibroblast growth factor receptors from liver vary in three structural domains. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):665–668. doi: 10.1126/science.1846977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell B. W., Afar D. E., Lew J., Douville E. M., Icely P. L., Gray D. A., Bell J. C. STY, a tyrosine-phosphorylating enzyme with sequence homology to serine/threonine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):568–572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Paulson K. E., Hanafusa H. Novel tyrosine kinase identified by phosphotyrosine antibody screening of cDNA libraries. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5541–5544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letwin K., Yee S. P., Pawson T. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase cDNAs related to fps/fes and eph cloned using anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):621–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lhoták V., Greer P., Letwin K., Pawson T. Characterization of elk, a brain-specific receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2496–2502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Expression cloning of an activin receptor, a predicted transmembrane serine kinase. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90549-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Edwards M. K., Anderson P. J. Control of muscle and neuronal differentiation in a cultured embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):165–167. doi: 10.1038/299165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemas D. S., Lindberg R. A., Hunter T. trkB, a neural receptor protein-tyrosine kinase: evidence for a full-length and two truncated receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):143–153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petch L. A., Harris J., Raymond V. W., Blasband A., Lee D. C., Earp H. S. A truncated, secreted form of the epidermal growth factor receptor is encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript in normal rat tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2973–2982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. The effect of protein context on nuclear location signal function. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. The mitotic inducer nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Ericsson L., Bratlien R. L., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by receptor phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90700-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Zheng P., Beidler D. R., Zerillo C. Spk1, a new kinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, phosphorylates proteins on serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):987–1001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobimatsu T., Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding the third polypeptide (gamma) of brain calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16082–16086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Shimanuki M., Yanagida M. Fission yeast genes that confer resistance to staurosporine encode an AP-1-like transcription factor and a protein kinase related to the mammalian ERK1/MAP2 and budding yeast FUS3 and KSS1 kinases. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):60–73. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. A., Jackson P., Baltimore D. The mouse type IV c-abl gene product is a nuclear protein, and activation of transforming ability is associated with cytoplasmic localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):669–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Zhang R. Relationship of a putative receptor protein kinase from maize to the S-locus glycoproteins of Brassica. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):743–746. doi: 10.1038/345743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut-Houri R., Hazum S., Givol D., Telerman A. The cDNA sequence and gene analysis of the human pim oncogene. Gene. 1987;54(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]