Figure 1.
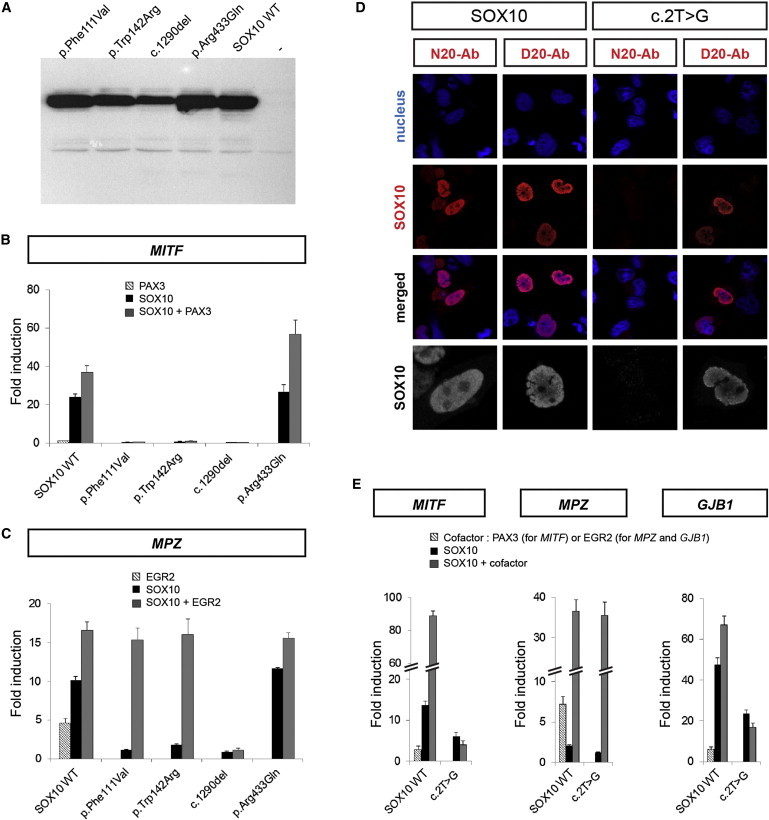
Functional Analysis of the Altered SOX10 Proteins
(A) Immunoblott analysis showing wild-type (WT) or altered SOX10 proteins with the use of an antibody directed against the carboxy terminal portion of the protein.
(B and C) Luciferase reporter-gene analysis. HeLa cells were cotransfected with the wild-type (WT) or altered SOX10 expression vector and a reporter construct containing the MITF promoter (B) or MPZ intronic enhancer (C) and known SOX10 cofactor expression vectors, i.e., PAX3 (B) or EGR2 (C). Reporter-gene activation is presented as luciferase fold induction relative to the empty vector. Results are the mean ± SEM of at least three different experiments, each performed in duplicate.
(D) Detection and localization of the c.2T>G (p.?) altered protein. HeLa cells were transfected with wild-type (left panels) or altered c.2T>G (p.?) (right panels) SOX10 constructs. Nuclei were counterstained with TO-PRO-3 iodide (blue). Transfected cells were immunostained with anti-SOX10 (red) directed against either the amino terminus (N20) or the carboxy terminus (D20) of the protein, as indicated. The merged images are presented below. A higher magnification of SOX10 labeling is also shown in gray (bottom panels).
(E) Luciferase reporter-gene analysis. HeLa cells were cotransfected with the wild-type (WT) or altered c.2T>G (p.?) SOX10 expression vectors and a reporter construct containing the MITF promoter (left panel), the MPZ intronic enhancer (central panel), or the GJB1 promoter (right panel) and the PAX3 (left panel) or EGR2 (central and right panels) expression vector. Reporter-gene activation is presented as fold induction relative to the empty vector. Results are the mean ± SEM of at least three different experiments, each performed in duplicate.
