Figure 5.
Mapping of CoTC Termination Activity in the CCNB1 3′ Flanking Region
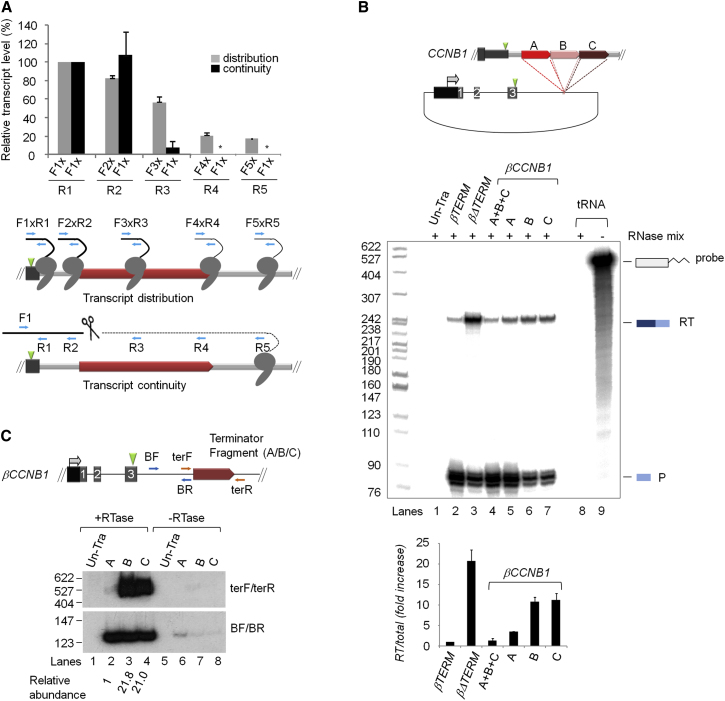
(A) Graph showing results of qRT-PCR analysis of transcript distribution (gray bars) and transcript continuity (black bars) at the CCNB1 gene terminator. Diagrams, below the graph, show primer pairs (blue arrows) used in transcript distribution and transcript continuity analyses. The CCNB1 poly(A) site (green arrowhead) and terminator element (red bar) are indicated. In the graph, (∗) indicates that no PCR product was detected with the indicated primer pairs. Error bars represent the results of three experimental repeats.
(B) RPA of CCNB1 terminator fragments. In the diagram of the βΔTERM reporter plasmid, dashed red lines indicate the insertion site of CCNB1 terminator fragments (labeled colored bars). Lane 1, untransfected cells, lanes 2–7 transfected cells. Control RNase digestion of the riboprobe is shown in lane 8 (tRNA+) beside undigested riboprobe (tRNA−, lane 9). For each sample RT and P protection products were quantified by PhosphoImage analysis and the relative abundance of the RT product (RT/Total) was calculated and displayed in the graph below the data panel. Error bars represent the results of three experimental repeats.
(C) qRT-PCR analysis of the continuity of CCNB1 terminator subfragment transcripts. In the diagram, the location of PCR primers (red and blue arrows), relative to terminator fragments (red bar) is shown. Lane 1, qRT-PCR of untransfected cells. Lanes 2–4, cells transfected with CCNB1 terminator fragment constructs. Lanes 5–8, control qRT-PCR of −RTase samples. cDNA in all samples was amplified using 15 PCR cycles (data not shown), which was determined to be within the linear range and therefore accurately reflects RNA abundance.
See also Figure S2.