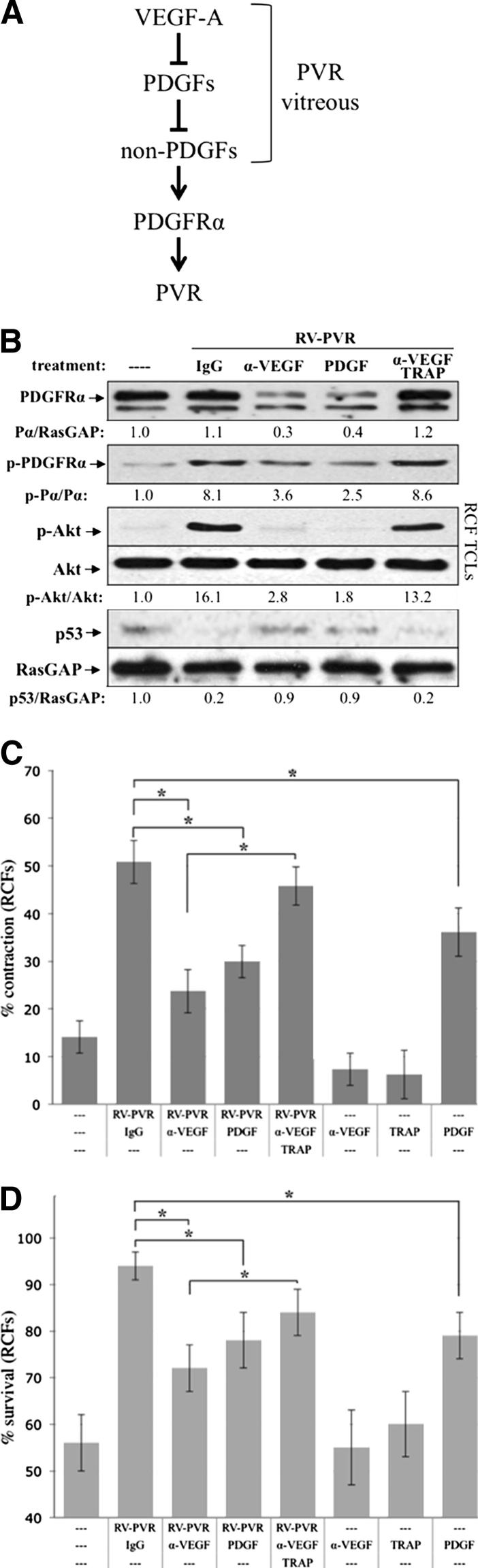
Figure 1.
Vitreous-driven signaling events and cellular responses associated with PVR were potentiated by vitreal VEGF-A. A: The functional relationship between three classes of growth factors present in PVR vitreous. VEGF-A antagonizes the action of PDGFs, which block non-PDGFs (growth factors outside of the PDGF family) that activate PDGFRα indirectly and thereby drive experimental PVR.37,39B: Neutralizing vitreal VEGF-A prevented PVR vitreous-driven signaling events. Primary RCFs were serum starved overnight and either lysed immediately without treatment (—) or continuously treated for 48 hours with 400 μL RV-PVR supplemented with 10 μg/mL nonimmune IgG, 25 μg/mL neutralizing anti-VEGF antibody, ranibizumab (α-VEGF), 20 ng/mL PDGF-A, or a combination of 10 μg/mL α-VEGF and 2 μmol/L PDGF TRAP. After treatment, cells were lysed and the resulting TCLs were subjected to Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies and quantified (see Materials and Methods). Ratios representing normalized band intensities are shown under each immunoblot. Blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. C: Neutralizing vitreal VEGF-A suppressed PVR vitreous-driven cell contraction. RCFs were preconditioned for 48 hours with serum-free medium alone (—) or 400 μL RV-PVR supplemented with 10 μg/mL nonimmune IgG, 25 μg/mL α-VEGF, 2 μmol/L α-VEGF + PDGF TRAP, or 20 ng/mL PDGF-A; in addition, cells were preconditioned with α-VEGF, PDGF TRAP, or PDGF-A alone as controls. After preconditioning, cells were transferred to collagen gels containing the same treatment and subjected to the collagen gel contraction assay. Gel area was measured after 24 hours. Data are presented as percentage contraction of collagen gels measured after 24 hours, and are represented as mean percentage contraction ± SDs obtained for three independent experiments. D: Neutralizing vitreal VEGF-A prevented PVR vitreous-driven cell survival. Near-confluent RCFs were placed in starvation medium (DMEM without serum) for 72 hours as an inducement of apoptosis, during which time they were conditioned with the same treatments as described in B. At 72 hours, surviving cells were quantified as those cells whose nuclei failed to stain positive for apoptosis (by TUNEL assay, see Materials and Methods). The graph presents data from three independent experiments showing the mean percentages of cells (± SD) surviving starvation. ∗P < 0.05 using a paired t-test. In each experiment, 12 randomly chosen fields were counted. Original magnification, ×100.