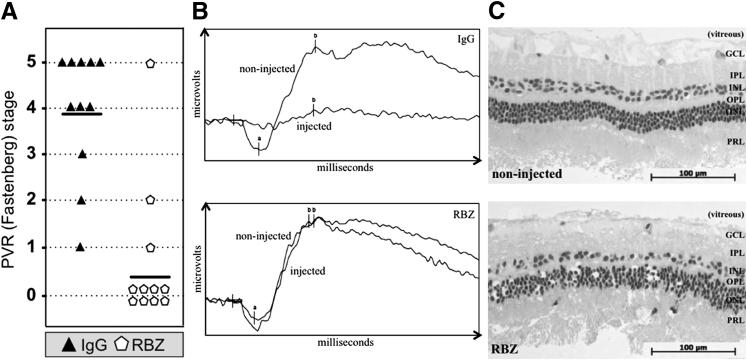
Figure 2.
Neutralizing vitreal VEGF-A safely and effectively prevented experimental PVR (A). One week after an intravitreal gas injection, rabbits received three separate 0.1-mL injections of PVR-inducing RCFs, PRP, and either 0.05 mg of α-VEGF ranibizumab (RBZ) or an equimolar amount of isotype control IgG. The concentration (calculated based on vitreous volume) of RBZ injected was 10-fold less than the amount typically used in human eyes.52,53 For each rabbit, only one eye was injected. Rabbits were examined and scored for development of PVR over a 4-week period; the results from the last time point (day 28) are shown, and the results from all other time points scored are shown in Supplemental Figure S3.Horizontal bars represent the mean PVR stage of each group (n = 11 for each group). Statistically significant differences at each time point were determined by Mann-Whitney analysis (P < 0.001). B: Treatment of rabbits with α-VEGF did not interfere with retinal function. Single-flash ERGs were obtained from rabbits on day 26 after injection; readouts were obtained for both injected and noninjected eyes of the same rabbit after dark adaptation. The ERGs shown span 100 milliseconds and are representative of three individual rabbits per group. The amplitude from the baseline to the a-wave trough (a) reflects the general physiological health of the outer retina (particularly the photoreceptors), while the amplitude from the a-wave trough to the b-wave peak (b) reflects the health of the inner retinal layers. RBZ-treated rabbit eyes elicited the same electrophysiological response as their noninjected counterpart eyes. Light-adapted, single-flash and light-adapted flicker ERGs also showed no significant difference between RBZ-injected and noninjected eyes (data not shown). C: Treatment of rabbits with RBZ did not cause major morphological changes in the retina. Eyes enucleated from a representative RBZ-treated rabbit (PVR stage 0) and a noninjected eye (PVR stage 0) were fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in methacrylate, divided into sections, and the resulting sections were stained with H&E. Representative IgG-treated rabbits had retinal detachments; thus, their morphological characteristics were not included in this analysis. A representative region of the neural retina is shown in each panel. Retinal layers are indicated: GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; PRL, photoreceptor layer. These data indicate that α-VEGF/RBZ treatment did not adversely affect the retina.