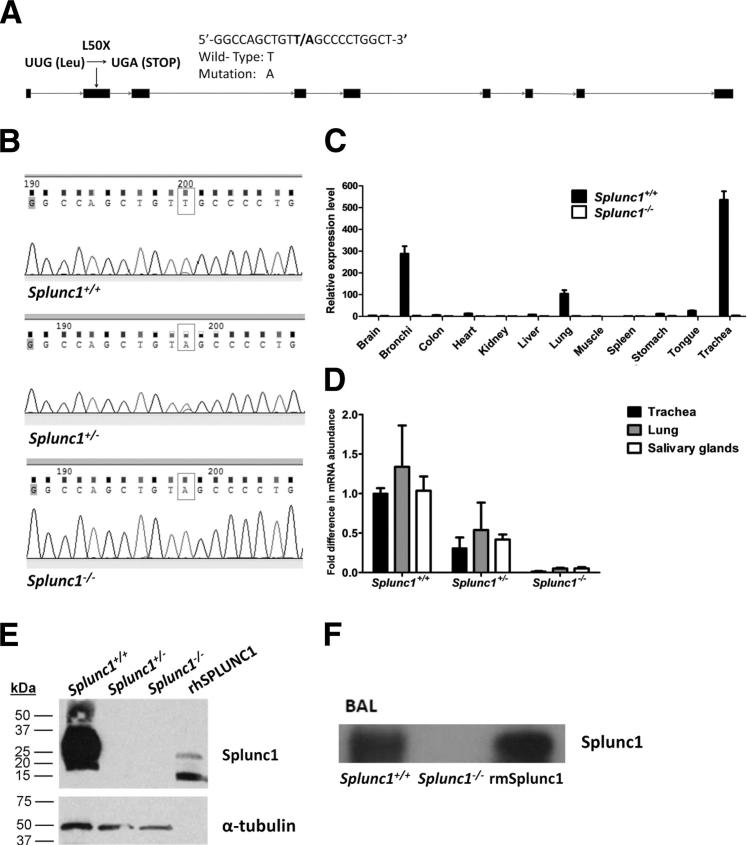
Figure 2.
Generation of Splunc1−/− mice and assessment of Splunc1 expression. A: Schematic of the mSplunc1 gene, depicting the location of a T→A point mutation in exon 2 in the knockout mice. Boxes represent exons. B: Sequencing based genotyping of Splunc1−/− mice. The PCR products amplified using genomic DNA from Splunc1+/+, Splunc1+/-, and Splunc1−/− mouse tail clips were verified by DNA sequencing. Top panel: Sequence of DNA products from a Splunc1+/+ mouse. Middle panel: Sequence of DNA products from a Splunc1+/- mouse. Bottom panel: Sequence of DNA products from a Splunc1−/− mouse. The boxes indicate the T→A mutation in the DNA molecules. C: Relative expression of mSplunc1 in various mouse tissues was analyzed by real time PCR and determined by the ΔΔCt method using mouse glucuronidase-β RNA as a control. D: The mSplunc1 mRNA expression was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR in mouse oral and respiratory tissues including trachea, total lung, and salivary glands. The mSplunc1 expression in Splunc1+/- and Splunc1−/− mice is expressed as fold decrease relative to Splunc1+/+ expression levels (n = 3 Splunc1+/+ animals, 3 Splunc1+/- animals, and 4 Splunc1−/− animals). E: Tracheal homogenates from Splunc1+/+ and Splunc1−/− mice were resolved on an SDS-PAGE gel (40 μg total protein/lane) and immunoblotted for mSplunc1 (upper blots). The last lane contains 250 ng of recombinant human SPLUNC1 protein (rhSPLUNC1) as a positive control for the SPLUNC1 antibody. Lower blots: As a loading control, the immunoblot was stripped and re-probed with an antibody recognizing mouse α-tubulin. F: BALF from Splunc1+/+ and Splunc1−/− mice was analyzed by immunoblot using anti-mSplunc1. The mSplunc1 protein was not detected in Splunc1−/− BALF. BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.