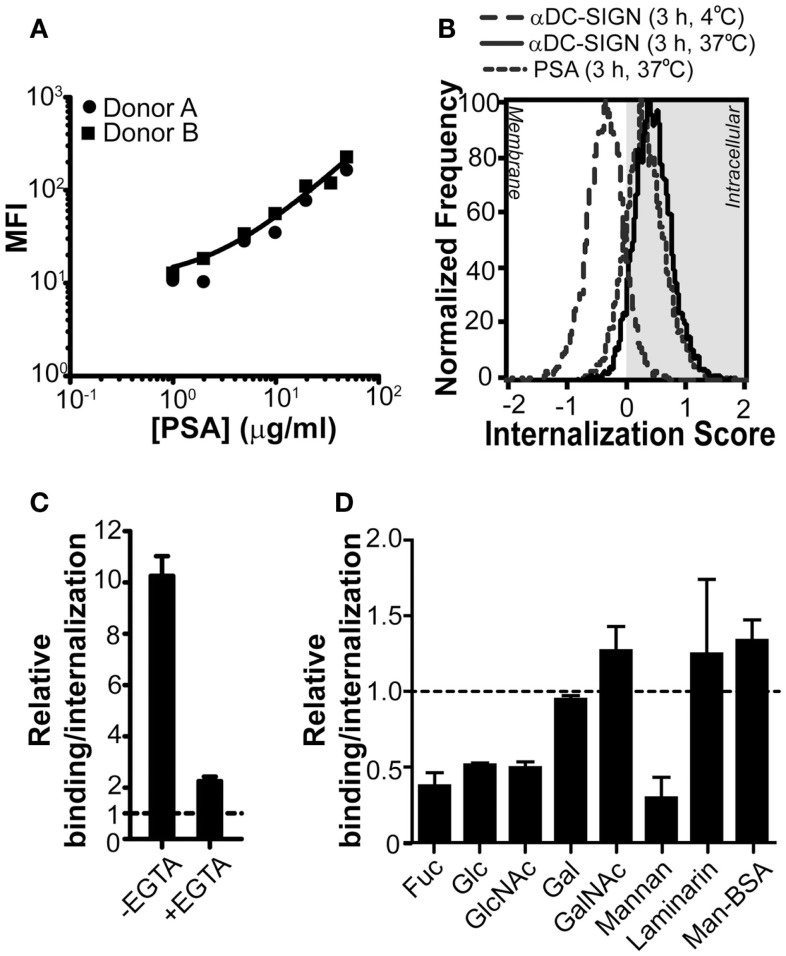
Figure 1.
PSA-binding/internalization by DCs can be blocked through Ca2+ chelation or by competition with glycans. (A) PSA is recognized by DCs. PSA-AF488 binding was evaluated by flow cytometry after 3 h of incubation at 37°C. The line represents the average median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the two donors. (B) PSA is internalized by DCs. Incubation of PSA-AF488 with DCs for 3 h at 37°C resulted in an efficient internalization of PSA. DCs incubated with a DC-SIGN-targeting antibody for 30 min at either 4 or 37°C were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. (C) PSA-binding/internalization is blocked by the addition of EGTA. Binding/internalization of PSA-AF488 by DCs was measured by flow cytometry in the presence of the Ca2+ chelator EGTA. Binding is shown relative to the autofluorescence of DCs. (D) PSA-binding/internalization is blocked by competition with mono and polysaccharides. GalNAc, α-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine; Fuc, α-l-fucose; Gal, d-galactose; Glc, d-glucose; GlcNAc, N-acetyl-d-glucosamine. Binding/internalization of PSA-AF488 by DCs was measured by flow cytometry after pre-incubation with the various mono and polysaccharides. Data is shown relative to DCs incubated with PSA in the absence of inhibitors. Data is shown as mean ± SD of a representative experiment out of six.