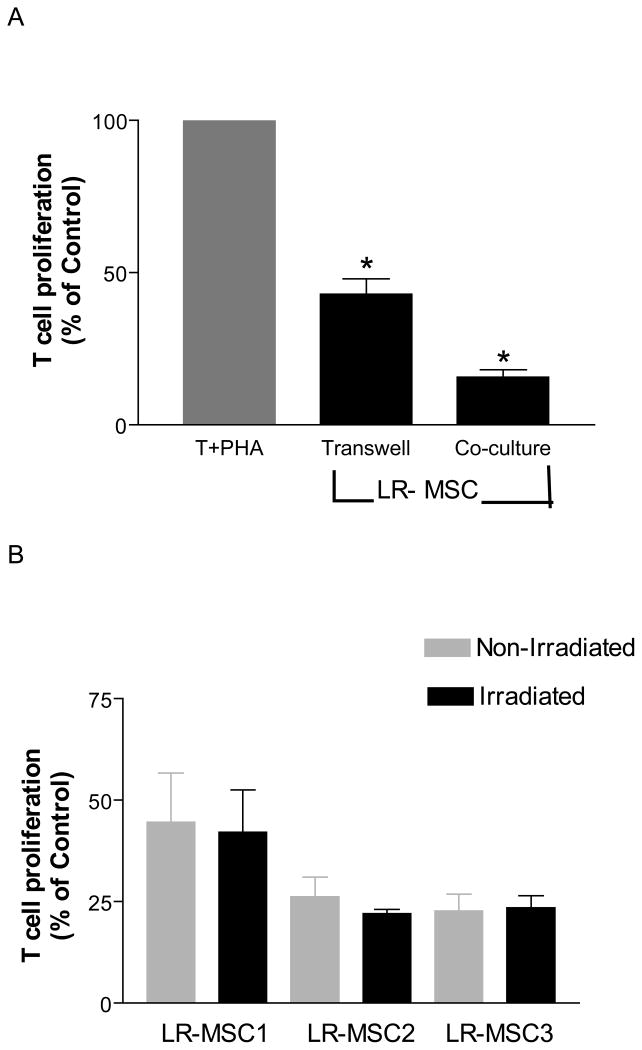
Figure 5. Both soluble mediators and cellular contact mediate Inhibitory effect of LR-MSCs on T cells proliferation.
A. 2×104 LR-MSCs/well (irradiated 30Gy) were plated onto the upper chamber of a 96-transwell plate in complete DMEM 4 hrs prior to the addition of 2×105 responder cells/well to the lower chamber in the presence or absence of PHA (10 μg/ml). The cells were cultured for 5 days with addition of [3H] thymidine in the last 18 hrs of culture. Co-cultures of LR-MSCs and T cells were performed as described in Figure 2. Suppression of T cell proliferation by LR-MSCs is shown for transwell and direct co-culture conditions. Data is presented here as a percentage of the T cell proliferations in response to PHA in the absence of LR-MSCs (100%) in their respective conditions. Data is shown for 10 LR-MSC lines. Significant inhibition of T cell proliferation was seen both in absence and presence of direct contact.*, p <0.001 vs. T +PHA. B. Irradiation of LR-MSCs does not alter T cell suppressive ability of LR-MSCs. Figure demonstrates % suppression of T cells in a transwell in presence of non-irradiated and irradiated LR-MSCs derived from 3 lung transplant recipients. No significant difference was noted between the two conditions (p=0.33).