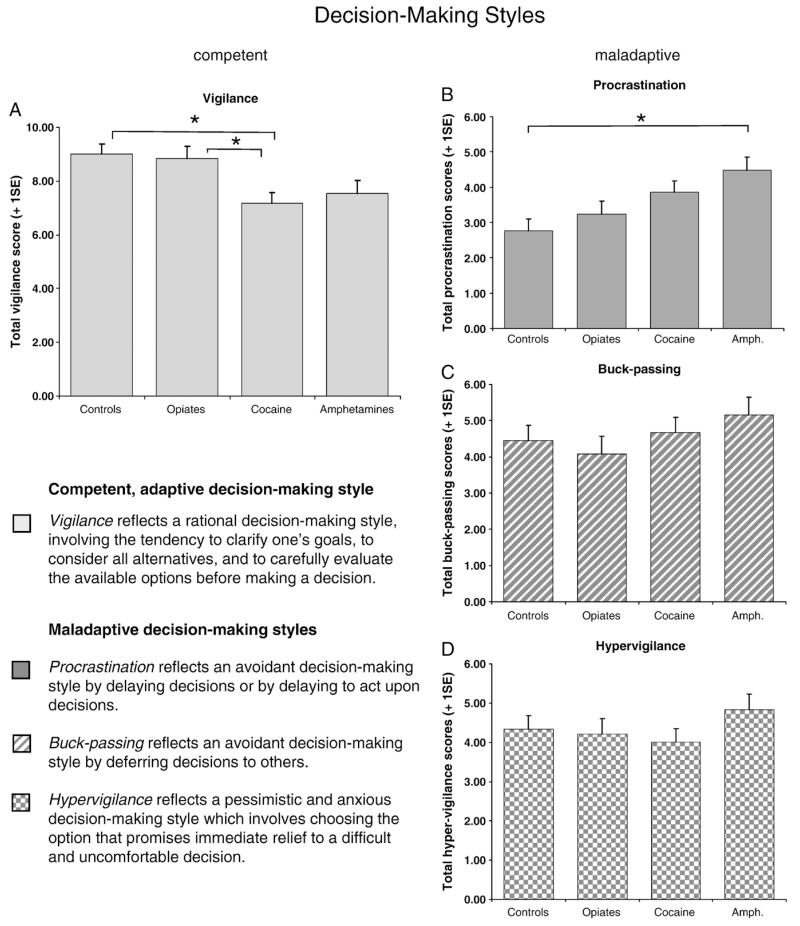
Fig. 1.
Decision-making styles, as assessed by the Melbourne Decision-Making Questionnaire (MDMQ), differed significantly between chronic drug users and healthy volunteers: (A) Stimulant-dependent but not opiate-dependent volunteers reported fewer rational decision-making compared with controls. (B) Amphetamine-dependent volunteers reported a significantly greater tendency to delay decisions than controls. No group differences were identified in terms of (C) buck-passing or (D) anxious (hypervigilant) decision-making styles.