FIG. 3.
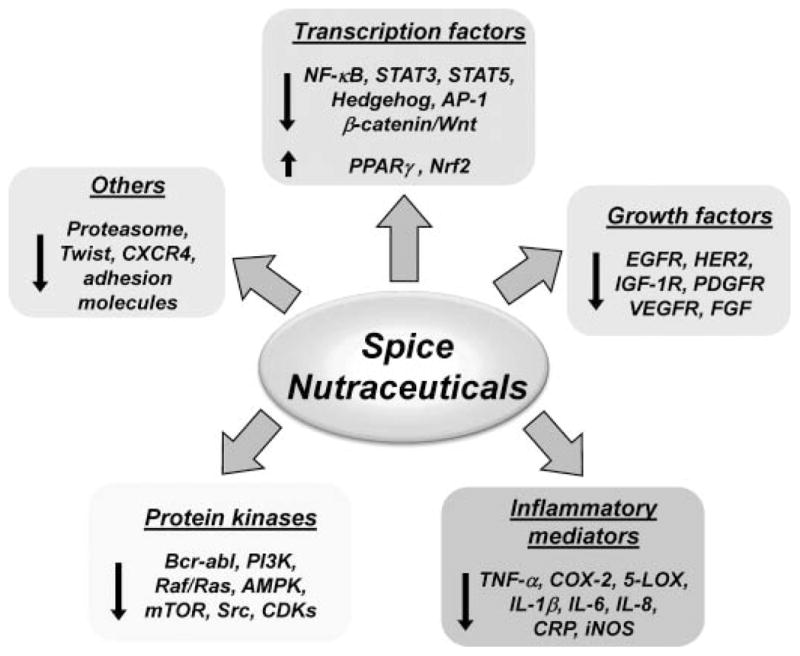
Molecular targets of spice-derived nutraceuticals in cancer. The nutraceuticals from spices modulates multiple targets including transcription factors, growth factors, and kinases involved in cancer cell growth, proliferation, survival, and metastasis. The single-head arrow indicates activation or positive regulation, whereas the blunt-end arrow indicates inhibition or negative regulation. 5-LOX indicates 5-lipoxygenase; AMPK, 5′ adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; AP-1, activator protein 1; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; CRP, C-reactive protein; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; IL-1β, interleukin 1beta; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; NRF-2, NF-E2-related factor 2; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; STAT3, signal transducer activator of transcription 3; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
