Figure 2. The induction of apoptosis by TAT-CTMP4 occurs via inhibition of the AKT pathway.
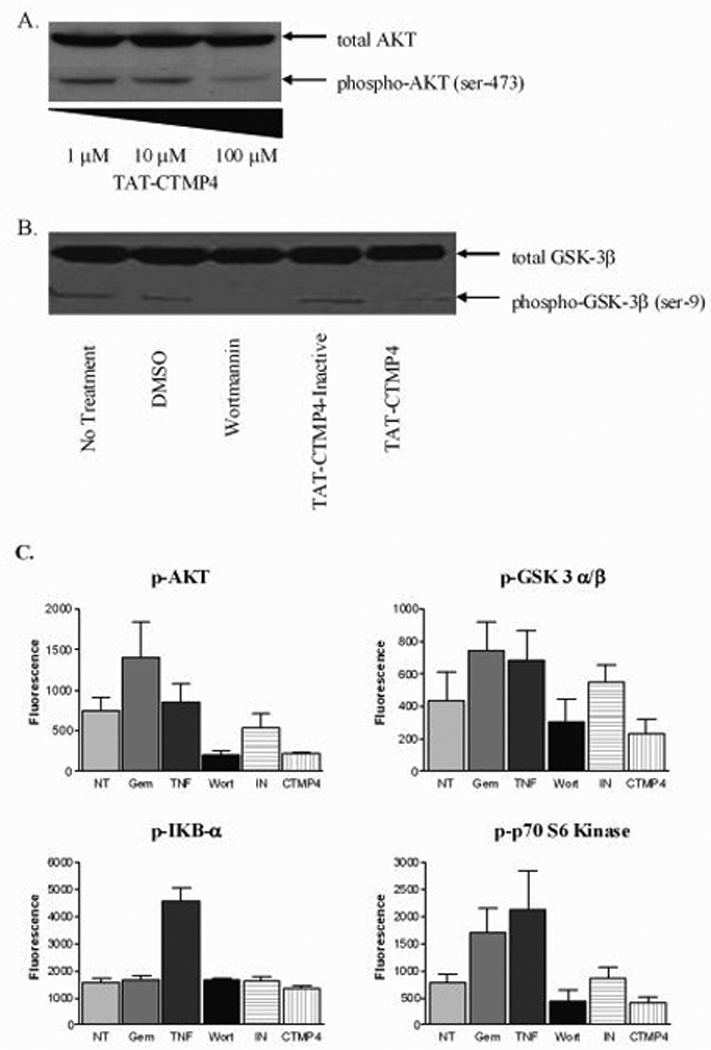
(A) Model human pancreatic adenocarcinoma (CFPAC-1) were treated with escalating doses of TAT-CTMP4. Samples were treated for 1 hour prior to preparation of cell lysates. Western blots were subsequently prepared and stained with anti-total AKT and anti-phospho-AKT (Ser473). (B) Panc-1 lysates were generated after exposure to PBS (no treatment control), DMSO (vehicle control for wortmannin), wortmannin (1 µM), TAT-CTMP4-Inactive (10 µM), and TAT-CTMP4 (10 µM) for 18 hours. Western blots were probed with anti-total GSK-3β and phospho-GSK-3α/β (Ser21/9). (C) Human model pancreatic adenocarcinoma (CFPAC-1) were treated with PBS (no treatment), gemcitabine (30 nM), recombinant human TNF-α (10 ng/ml), wortmannin (1 µM), TAT-CTMP4-Inactive (10 µM), and TAT-CTMP4 (10 µM). One hour later, cell lysates were generated and phospho-proteins were quantitated by bioplex analysis. Each experimental group represents an n=4. Results are expressed as the mean, with bars representing standard error of the mean.
