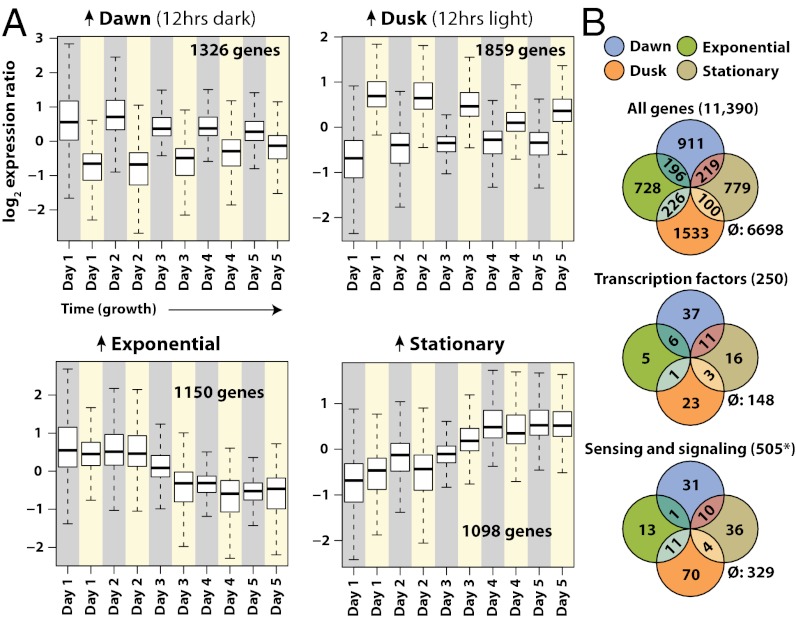
Fig. 1.
Four principal genome-wide expression patterns observed over the growth cycle. (A) The mean and quantiles of expression ratios for state-associated genes are shown over time during the course of the experiment. Gene groups consist of genes whose expression changes were significantly associated with dark:light or exponential:stationary transitions by ANOVA at P < 0.01. Dawn-associated genes were significantly associated with the dark:light transition and higher in expression at the end of the 12-h dark periods (gray backgrounds). Dusk-associated genes were significantly associated with the dark:light transition and higher in expression at the end of the 12-h dark light (yellow backgrounds). Exponential and stationary genes were significantly associated with the exponential:stationary transition. Genes labeled exponential were higher in expression during the exponential phase (up to day 3). Genes labeled stationary were higher in expression during the stationary phase (following day 3). (B) Euler diagrams illustrate the numbers of genes associated with each condition. Genes for which associations were not detected are indicated by the ∅ symbol. *Sensing and signaling genes include all photoreceptors and genes with the following InterPro domains: IPR000719 (protein kinase), IPR001019 (G protein alpha subunit), IPR001632 (G protein beta subunit), IPR001789 (response regulator receiver), IPR003018 (GAF), IPR000337 (GPCR, family 3), IPR000276 (GPCR, rhodopsin-like), IPR002182 (NB-ARC), IPR001806 (Small GTPase), IPR002073 (cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase), IPR001054 (guanylyl cyclase), IPR000014 (PAS), IPR001680 (WD40), IPR001611 (Leucine-rich repeat (LRR)). WD40 and LRR domains (110 and 81 genes) are multifunctional and may not all represent signaling genes.