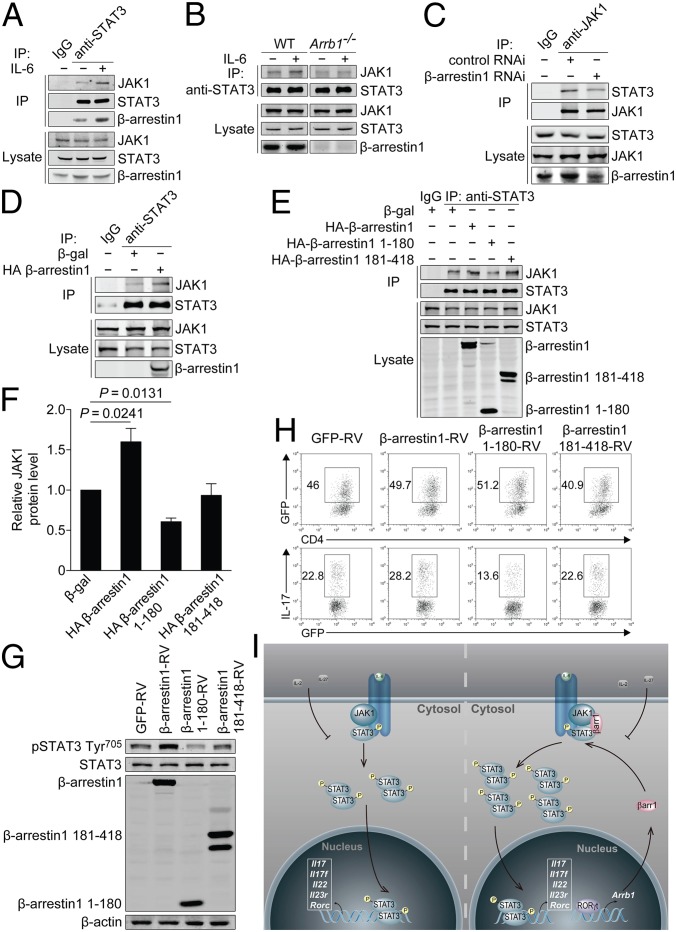
Fig. 7.
Interaction of JAK1/β-arrestin1/STAT3 regulates STAT3 activation and TH17 cell differentiation. (A) Endogenous interaction of JAK1/β-arrestin1/STAT3 in naïve CD4+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice. (B) Endogenous interaction of JAK1 and STAT3 in naïve CD4+ T cells from Arrb1−/− mice and WT littermates. (C and D) Endogenous interaction of JAK1 and STAT3 in HEK293 cells expressing control RNAi or β-arrestin1 RNAi (C) or β-gal or HA–β-arrestin1 (D). (E) Endogenous interaction of JAK1 and STAT3 in HEK293 cells expressing β-gal, HA–β-arrestin1, HA–β-arrestin1 1–180, or HA–β-arrestin1 181–418. (F) Densitometric analysis of E. (G) Immunoblot of phosphorylation and expression of STAT3 in naïve CD4+ T cells transduced with β-arrestin1–RV, β-arrestin1 1–180-RV, β-arrestin1 181–418-RV, or GFP-RV under TH17-polarizing conditions. (H) Flow cytometry of intracellular IL-17 in naïve CD4+ T cells transduced with β-arrestin1–RV, β-arrestin1 1–180-RV, β-arrestin1 181–418-RV, or GFP-RV under TH17-polarizing conditions. (I) Schematic model of JAK1/β-arrestin1/STAT3 interaction in TH17 cells. βarr1, β-arrestin1.