Fig. 4.
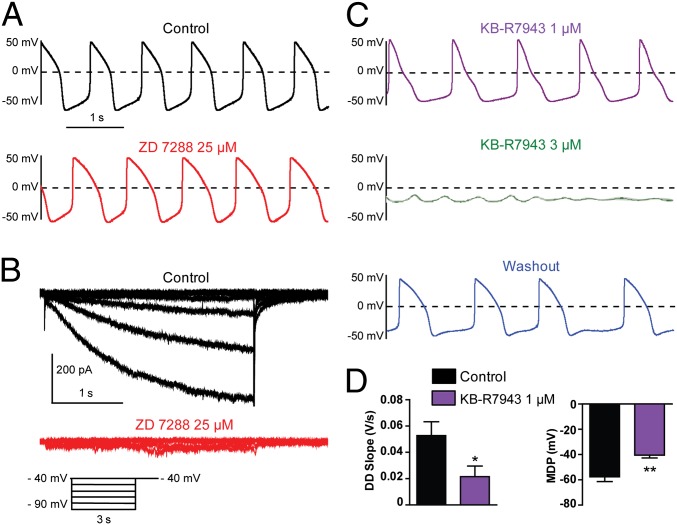
A subset of hESC-CMs with prominent If-independent pacemaker is insensitive to ZD7288 but responsive to KB-R7943. (A–C) Combined current- and voltage-clamp recordings were performed in the same cell. (A, Upper) Spontaneous AP pattern of an hESC-CM recorded under current-clamp in control conditions. (B) The If current was subsequently recorded in the same cell, under voltage-clamp, in the absence (black traces) and presence of 25 µM ZD7288 (red traces) by stepping the membrane from a holding potential of −40 mV to −90 mV in 10-mV decrements for 3 s pulse duration. Once If current inhibition by ZD7288 was monitored under voltage-clamp, the AP pattern of the same cell was examined under current-clamp, during continuous ZD7288 exposure; note the lack of significant effect on pacing (see A, Lower). (C, Top) Following ZD7288 washout, the same cell was exposed to 1 µM KB-R7943 (violet trace); notice the bradycardia, the MDP depolarization, and the decreased DD slope. (Middle) The same cell was subsequently perfused with 3 µM KB-R7943 (green trace), leading to a rapid and complete loss of pacemaker activity. (Bottom) The same cell was washed out and partially recovered its pacemaker (blue trace). (D) KB-R7943 (1 µM) significantly decreased the DD slope (*P = 0.0482, n = 6) and depolarized the MDP (**P = 0.0091, n = 6) in this subset of cells.