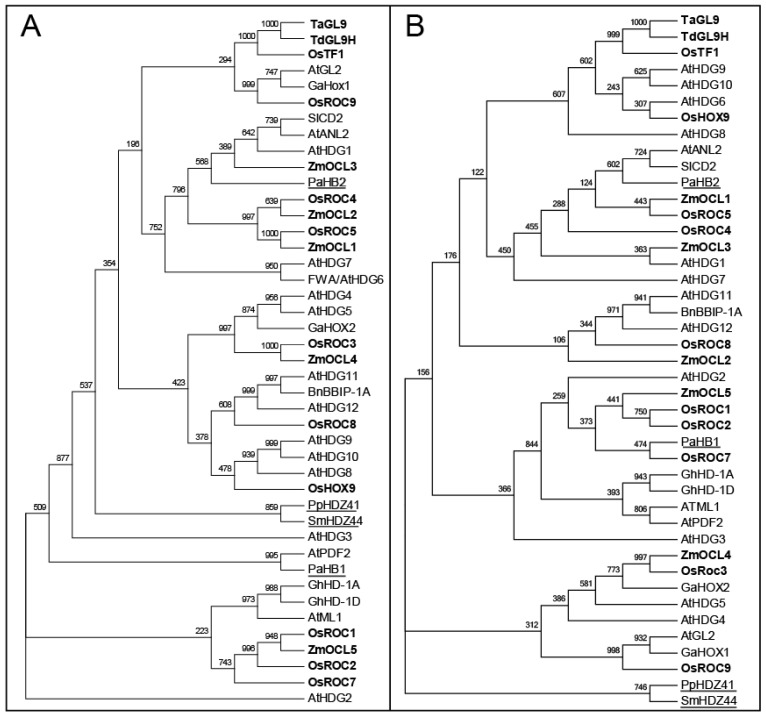
Figure 1.
Unrooted phylogenetic tree of selected HD-Zip IV proteins. HD-Zip IV protein sequences were retrieved from the NCBI database and aligned with CLUSTALX [47]. Unrooted phylogenetic trees were constructed based on aligned protein sequences using the Neighbor-Joining algorithm [48] with a Bootstrap value of 1000 from CLUSTALX [47]. Species of origin are indicated by two-letter prefixes. The accession numbers of the published protein sequences used in the phylogenetic trees are listed in Table 1; unpublished BnBBIP-1A has Accession ABA54874. (A) Phylogenetic tree based on full-length amino acid sequences of 43 HD-Zip IV proteins; (B) Phylogenetic tree constructed using HDs of selected HD-Zip IV proteins (60–61 amino acid residues). The HD sequences that were included in the analyses were selected by a Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (SMART) [49]. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Pa, Picea abies; Ga, Gossypium spp; Gh, Gossypium hirsutum; Zm, Zea mays; Os, Oryza sativa; Ta, Triticum aestivum; Td, Triticum durum; Sl, Solanum lycopersicum; Bn, Brassica napus; Pp, Physcomitrella patens; Sm, Selaginella moellendorffii. Proteins from mono- and dicotyledonous groups are indicated in bold and normal types, respectively. Picea abies, Physcomitrella patens and Selaginella moellendorffii have not been assigned to either group (underlined).