Figure 1.
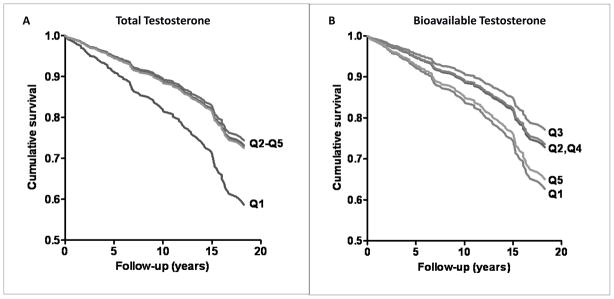
A. Total testosterone and 20-year incident CHD in women (adjusted for age, BMI, WHR, smoking, exercise, alcohol). B. Bioavailable testosterone and 20-year incident CHD in women (adjusted for age, BMI, WHR, smoking, exercise, alcohol) (Laughlin GA, Goodell V, Barrett-Connor E. Extremes of endogenous testosterone are associated with increased risk of incident coronary events in older women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;95:740–7, Copyright 2010, The Endocrine Society).
